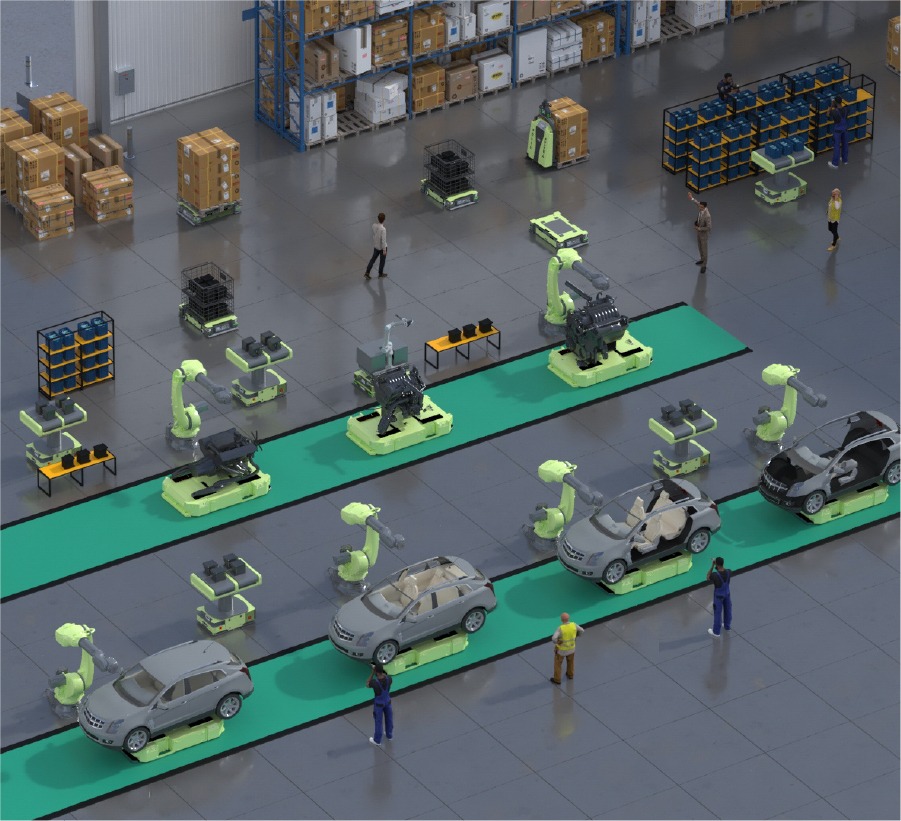
Safety is the first—and sometimes the biggest—concern companies have when considering AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots). When machines move autonomously inside busy factories and warehouses, the stakes are high:
- People work nearby
- Forklifts cross paths
- Aisles narrow unexpectedly
- Material stacks change daily
- Speed and urgency increase during peak hours
This is why modern AGV/AMR systems are designed with multi-layered safety architecture, advanced sensing, and certified controls that make autonomous robots safer than forklifts, pallet trucks, or manual trolleys.
This blog explains exactly how AGVs and AMRs keep your facility safe using sensors, logic, software controls, standards, and real-time decision-making.
Why Safety Matters in Autonomous Material Movement
Manual movement is one of the biggest sources of workplace accidents.
- Forklifts cause thousands of injuries each year
- Pedestrian–vehicle collisions are common
- Blind corners, intersections, and tight aisles amplify risk
- Fatigue, distraction, and inconsistency contribute to errors
AMRs and AGVs remove human error, enforce predictable movement, and follow strict rules — making operations safer and more reliable.
Safety is not a feature for autonomous robots.
It is the foundation.
Discover how the right Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) solutions drive business efficiency.
Download our free eBook for expert insights and trends!
The Multi-Layer Safety System Inside AGVs & AMRs
Modern mobile robots follow a layered protection model:
- Environment Awareness (sensors)
- Real-time decision-making (software)
- Motion control (hardware + algorithms)
- Certified safety circuits (ISO-compliant controls)
Each layer acts as an independent shield, creating redundancy and ensuring predictable behavior even in dynamic environments.
1. Perception Safety: How Robots See the World
AGVs and AMRs rely on multiple sensors to understand obstacles, people, and surrounding infrastructure.
2D / 3D LiDAR Scanners
- Provide 270° to 360° visibility
- Detect objects within millimeters
- Measure distance, shape, and motion
- Used for navigation + safety laser fields
LiDAR is the robot’s primary safety eye.
Depth Cameras & Stereo Vision
- Recognize pallets, humans, and shelf faces
- Support pallet alignment
- Enhance detection in complex environments
Ultrasonic Sensors
- Detect close-range obstacles
- Helpful for low-lying or small objects
Infrared Sensors
- Useful for reflective surfaces
- Enhance near-field protection
IMU & Wheel Sensors
- Track robot orientation and movement
- Detect skidding, sliding, or unexpected shifts
Robots combine all sensor inputs to build a real-time safety map of their environment.
2. Safety Fields: How Robots Respond to Humans & Obstacles
AGVs and AMRs don’t just detect obstacles — they respond intelligently based on threat level.
They use three automatic safety zones:
Warning Zone (Outer Zone)
Robot slows down when something is detected at a distance.
This communicates intention and prevents abrupt stops.
Protection Zone (Middle Zone)
Robot reduces speed sharply and prepares to stop.
Safety Zone (Inner Zone)
Robot performs a full emergency stop within milliseconds.
This ensures:
- Zero contact
- Zero collision
- Zero unsafe behavior
Safety zones adjust dynamically based on:
- speed
- direction
- turning angle
- load status
- people around
- aisle width
No human-driven vehicle can respond this consistently.
3. Obstacle Handling: AGV vs AMR Behavior
How AGVs Handle Obstacles
AGVs typically stop and wait when an obstacle appears, because they follow fixed paths.
This makes AGVs predictable — but less flexible.
How AMRs Handle Obstacles
AMRs use LiDAR + AI to:
- slow down
- alter path
- take alternate routes
- negotiate tight spaces
- avoid people smoothly
This makes AMRs ideal for mixed human-robot environments.
4. Motion Control Safety
AGVs and AMRs monitor how the robot moves, not just what’s around it.
Key Motion Safety Controls
- Speed limiting
- Smooth acceleration
- Predictive deceleration
- Tilt/roll detection
- Load stability checks
- Cornering speed limits
- Anti-sway and anti-slip logic
If anything behaves unexpectedly — the robot pauses or stops.
5. Fail-Safe Controls & Redundant Safety Systems
Robots are built with redundancy — if any critical safety component fails, the robot defaults to “safe stop.”
Examples:
- Dual-channel emergency circuits
- Redundant LiDAR coverage
- Backup sensors
- Battery cutoff mechanisms
- Watchdog controllers
- Secondary computers for safety logic
Compliance with standards ensures global-grade safety.
6. Global Safety Certifications & Standards
Professional AGV/AMR systems follow international safety frameworks:
- ISO 3691-4 (primary AMR/AGV safety standard)
- ISO 13849 (safety-related control systems)
- CE Marking
- UL Certification
These guarantee that robots operate safely around people, equipment, and material.
7. Safety in Human–Robot Collaboration
Modern facilities are shifting from separation to collaboration.
How AMRs Work Safely with People
- Speed reduction in shared aisles
- Predictive human motion tracking
- Slow-and-pass behavior
- Hand gesture detection (advanced systems)
- Automatic standstill on close approach
How AGVs Work Safely with People
- Fixed predictable paths
- Audible and visual alerts
- Virtual safety zones
- Stop-on-encounter logic
Both systems reduce risk dramatically compared to manual forklifts.
8. Safety in Complex Scenarios
Intersections & Cross-Traffic
Robots follow virtual traffic rules:
- right-of-way
- intersection control
- reservation-based crossing
Narrow Aisles
Robots reduce speed automatically.
Blind Spots
LiDAR “sees” around corners via reflection patterns.
Elevators
Integrated sensors ensure doors open, clear space is available, and weight limits are respected.
Dock Areas
Robots check alignment and floor edge boundaries before moving.
9. Safety During Charging & Maintenance
Charging Safety
- auto-docking alignment
- temperature monitoring
- voltage/current protection
- fallback shutdown logic
Maintenance Mode
- locked-out movement
- disabled motors
- manual overrides
- safety light indicators
Robots communicate their state clearly to avoid any confusion.
10. How AGVs & AMRs Make Facilities Safer
Compared to forklifts and manual movement:
- Zero distracted driving
- Zero fatigue
- Zero aggressive maneuvers
- Zero unexpected reversing
- Zero shortcuts
- Zero alcohol/drug influence
- Near-zero collision risk
Facilities see:
- up to 95% fewer movement incidents
- drastically lower insurance claims
- safer traffic flow
- more predictable operations
Discover how the right Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) solutions drive business efficiency.
Download our free eBook for expert insights and trends!
Common Mistakes Companies Make About Robotics Safety
- Assuming robots behave like humans
- Ignoring Wi-Fi/network impact
- Not training operators and pedestrians
- Poorly designed traffic lanes
- Mixing forklifts and robots without rules
- No defined safety responsibilities
- Rushing full deployment without piloting
Safety culture + robot safety = true operational excellence.
Conclusion
AGVs and AMRs are among the safest automation technologies in modern intralogistics. With multi-sensor perception, certified safety controls, dynamic obstacle handling, and predictable movement logic, they dramatically reduce risk for people, products, and infrastructure.
A well-designed autonomous fleet brings not only efficiency — but peace of mind.
How Novus Hi-Tech Supports Safe, Scalable Automation
Novus Hi-Tech builds AI-driven AGV & AMR systems engineered with safety at their core. As a global pioneer in autonomous robotics — developed indigenously in India — Novus brings:
- 150+ patents
- 1,200+ robots deployed
- 8M+ km of autonomous travel
- 100+ enterprise customers worldwide
Our safety engineering framework includes:
- facility safety audits
- risk assessment studies
- traffic-flow design
- ISO 3691-4 compliant robot systems
- training for operators & pedestrians
- continuous monitoring & optimization
📩 If you want to safely introduce AGVs or AMRs into your operations:
mailto:marketing@novushitech.com
Together, we can build a safer, smarter, and more efficient facility — one autonomous movement at a time.