Imagine dashing across a foggy highway, seeing less than a few meters ahead. Then your car’s warning system informs you of an obstacle well before you’re able to spot it. How? Depth sensing – an advanced technology that is changing the game for vehicle safety. Depth sensing is playing an instrumental role in making roads comply with accident free travel, from autonomous vehicles to driver-assistance systems. But what exactly does it do, and how does it work? Let’s delve into it.
What Is Depth Sensing and How Does It Work?
Depth sensing is the property of the system where it can measure the distance between objects through specialized technologies. It helps vehicles and machines become aware of their environment in a three-dimensional fashion, a more precise and useful simulation of human vision. Recognition of distances of surrounding objects aids navigation, obstacle detection, and collision prevention.
Depth-sensing technologies develop an elaborate environment map by using light projections, laser pulses, or stereo vision. They form an exact map of the surroundings allowing a vehicle to act based upon real-time data and split-second decisions on the matter of safety.
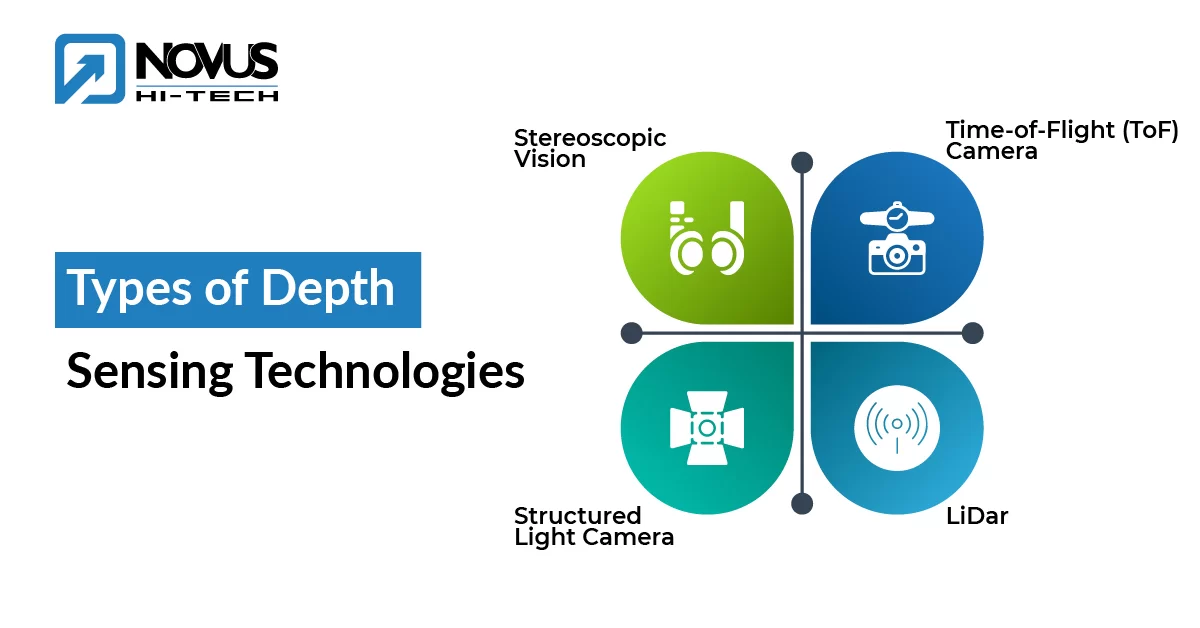
Types of Depth Sensing Technologies
Various depth sensing technologies work under the hood of modern safety systems. Each, of course, has specific benefits. Here are the most widely used techniques:
1. Stereoscopic Vision
Stereovision is where two cameras capture an image at different angles to simulate human binocular vision. It compares images from both cameras for disparity measurement for depth calculation. Such tasks have been incorporated into LANESIDE and pedestrian detection systems’ advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
2. Time-of-Flight (ToF) Camera
The time of Flight camera calculates the time taken for light to come into contact with an object, bounce back, and return to the device. It computes depth within the device’s field of view by this delay. ToF technology performs very well in dimly lit locations and is involved in automatic braking systems.
3. Structured Light Camera
A structured light camera projects a known pattern, be it dots or grids, onto a surface. It then conducts an analysis on the distortion of that particular pattern to ascertain depth. This is used in facial recognition systems and vehicle cabin monitoring for the detection of driver alertness.
4. LiDar
LiDars send laser pulses toward an object and measure the time it takes for that pulse to reflect off the object and the distance to the object. LiDars create 3D maps of the environment with high resolution. In self-driving cars, they are integral to precisely detecting obstacles and navigating through challenging weather.
Applications of Depth Sensing in Autonomous Systems
Depth sensing, beyond applications of their use on vehicles, is radically transforming different industries. Here is how:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
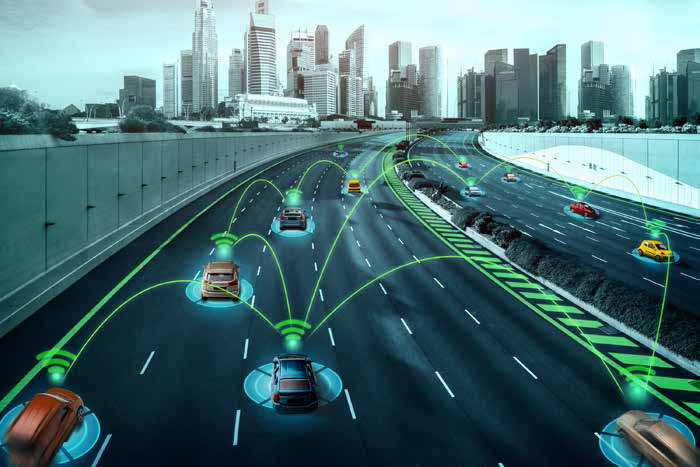
Self-driven car technology exploits depth sensing to know what it is dealing with, for instance, pedestrians may be detected, lane marking defined, or hazard predictions made, all by techniques such as LiDAR and stereo vision. In so doing, they enhance safety on roads through their ability to make split-second decisions.
2. Industrial Robotics
Manufacturing robots employ depth sensing to accurately pick, switch, and locate objects in factories while avoiding collision between them. Automated assembly lines employ such techniques for economic sorting, packaging, and quality control.
3. Security and Surveillance
Depth sensing enhances the security systems by providing advanced facial recognition matching, physical motion detection, and an estimate of people counts in the places under surveillance. Surveillance cameras employ ToF sensors and structured lights to obtain accurate monitoring in restricted areas.
4. Medical Imaging and Monitoring
In medicine, depth sensing is being utilized in high-tech imaging methods like 3D ultrasound scans and remote patient monitoring. ToF cameras track the movements of surgery patients in assisted living facilities, reducing the risks that the patients might face.
5. Augmented and Virtual Reality
Depth sensing enhances the AR/VR experience by adding a realistic path for spawning 3D environments. Various devices like Microsoft’s HoloLens and Apple’s Face ID make use of structured light and various time-of-flight sensors to maintain accurate motion tracking.
A Brief Insight on Novus Hi-Tech’s Contributions to Depth Sensing Solutions
Novus Hi-Tech is at the helm of the depth-sensing innovation process as a provider of sophisticated solutions for automotive safety. Armed with advanced technology in LiDAR, Time of Flight, and stereo vision systems, Novus Hi-Tech caters to automotive manufacturers with state-of-the-art depth-sensing technologies. The focus of their development and research includes enhancing ADAS abilities, accident reduction, and driving truly autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
Depth sensing is not merely a technological option, but it is a safety feature that draws the lines between where transport is heading to. No matter whether stereo vision or TOF, lasers, or LiDAR, these solutions allow the vehicles to visually see their surroundings like never before. As industry leaders innovate, Novus Hi-Tech being one of them, we reach into a safer world with intelligent transportation systems.
FAQs
- What does a 2MP depth sensor do?
A 2MP depth sensor captures depth information by measuring distances between objects. It enhances portrait photography, improves augmented reality applications, and assists in vehicle safety systems.
- What is the difference between LiDAR and ToF?
LiDAR uses laser pulses to create high-resolution 3D maps, while ToF cameras measure the time light takes to return after bouncing off an object. LiDAR is more precise for long-range applications, whereas ToF is ideal for short-range depth sensing.
- What is the use of a depth sensor?
Depth sensors are used in autonomous vehicles, robotics, security systems, medical imaging, and AR/VR applications to map surroundings, detect obstacles, and enhance user interaction.
- What are three remote sensing techniques?
The three primary remote sensing techniques are passive remote sensing (using natural light or heat emissions), active remote sensing (using LiDAR or radar to send signals and analyze returns), and multispectral/hyperspectral imaging (capturing data in multiple wavelengths for detailed analysis).