The Growing Demand for Efficiency and Automation in Warehouses
In today’s fast-paced world, efficiency and automation are not just desirable but essential for staying competitive. This need is vividly reflected in the market projections. By 2025, the global market for warehouse automation is expected to reach a staggering $30 billion. This exponential growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for efficiency and the need to reduce operational costs across industries.
The Rise of Intralogistics Robots
Amid this wave of automation, intralogistics robots have emerged as a revolutionary force, fundamentally transforming the landscape of warehouse operations. These advanced robots are not just a futuristic concept but a present-day reality, reshaping how warehouses function and paving the way for smarter, more efficient supply chains.
Intralogistics robots are designed to handle a variety of tasks within a warehouse setting, from transporting goods and managing inventory to sorting and picking items with incredible precision. Their integration into warehouse systems signifies a significant leap towards fully automated, highly efficient, and cost-effective warehouse management.
Discover how Intralogistics Robots transform warehouse efficiency.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
Understanding Intralogistics Robots
Definition and Overview
Intralogistics robots are autonomous or semi-autonomous mobile robots designed to automate tasks within warehouses and distribution centers. These robots are engineered to handle a wide range of operations, from transporting goods and managing inventory to sorting and picking items, significantly enhancing efficiency and productivity in intralogistics processes.
Evolution of Intralogistics Automation
The journey of intralogistics automation has seen a significant transformation over the years. Traditionally, warehouses relied heavily on manual labor for tasks such as picking, packing, and transporting goods. This manual approach was not only time-consuming but also prone to errors and inefficiencies.
With the advent of technology, the first wave of automation introduced conveyor belts, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), and basic mechanized solutions. While these advancements improved efficiency, they still required substantial human oversight and intervention.
The current era of intralogistics automation is characterized by the deployment of advanced robots. These intralogistics robots leverage cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sophisticated sensor systems to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. This shift towards robot-powered solutions has revolutionized warehouse operations, enabling higher productivity, accuracy, and safety.
Key Characteristics of Intralogistics Robots
1. Mobility and Autonomy
Intralogistics robots are designed with high mobility and autonomy, allowing them to navigate complex warehouse environments independently. Equipped with advanced sensors, such as LiDAR, cameras, and proximity detectors, these robots can map their surroundings, detect obstacles, and adjust their paths in real-time. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) use AI algorithms to make intelligent decisions on the go, ensuring smooth and efficient operations without the need for human guidance.
2. Versatility and Adaptability
One of the most significant advantages of intralogistics robots is their versatility and adaptability. Different types of robots can handle a variety of tasks, from picking and placing individual items to palletizing and transporting heavy loads. For instance, robotic arms are adept at precision tasks like picking and packing, while automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and AMRs excel in transporting goods across the warehouse. This adaptability allows businesses to deploy robotic solutions tailored to their specific needs, optimizing various aspects of their intralogistics processes.
3. Collaboration with Humans
Intralogistics robots are designed to work safely and efficiently alongside human workers, creating a collaborative environment that enhances overall productivity. Advanced sensors and safety features ensure that robots can operate in close proximity to humans without causing accidents or injuries. This human-robot collaboration allows robots to handle repetitive and strenuous tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities. The synergy between robots and humans leads to a more efficient and harmonious workflow, maximizing the strengths of both parties.
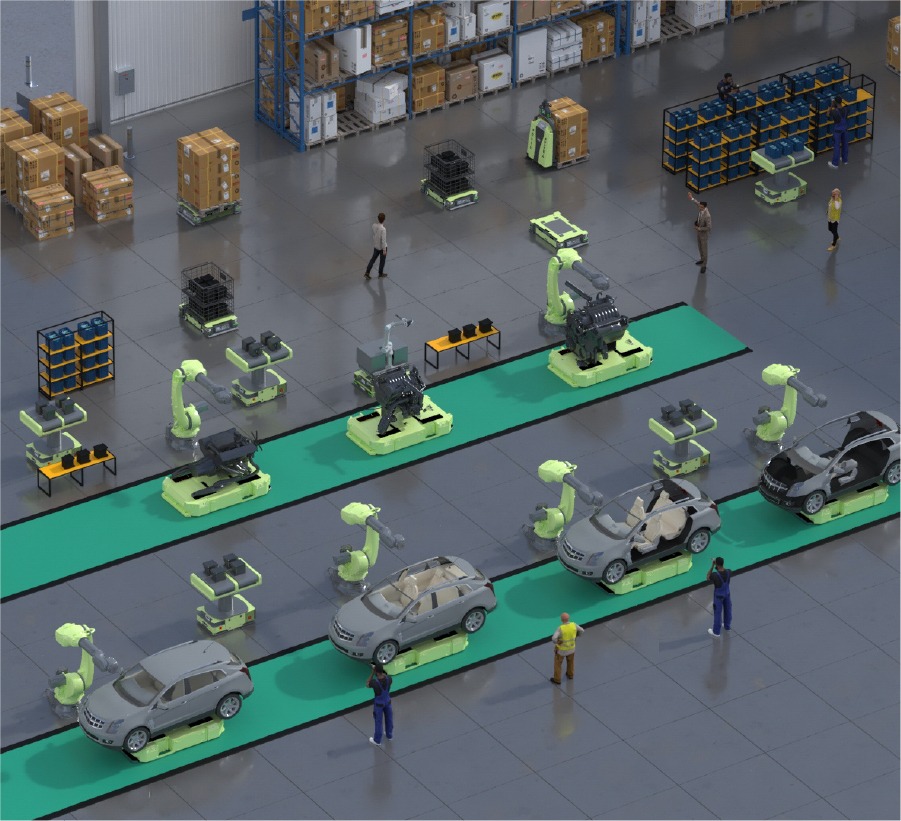
Types of Intralogistics Robots
Intralogistics robots come in various forms, each tailored to specific functions and capabilities within warehouse and distribution center environments. Here, we explore the main categories of these robots, highlighting their unique features and the roles they play in optimizing intralogistics operations.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Function and Capabilities:
- Independent Navigation: AMRs navigate warehouse environments autonomously using advanced sensor systems, including LiDAR, cameras, and infrared sensors. These sensors enable the robots to create and update maps of their surroundings, detect obstacles, and dynamically adjust their routes to avoid collisions.
- Tasks: AMRs are highly versatile, handling a range of tasks such as goods-to-person picking, where they transport items from storage locations to human workers for packing or further processing. They can also perform delivery tasks, moving goods across different areas of the warehouse.
- Benefits: The independence and flexibility of AMRs reduce the need for fixed infrastructure like conveyor belts, allowing for more adaptable and scalable warehouse layouts.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Function and Capabilities:
- Predetermined Paths: Unlike AMRs, AGVs follow predetermined paths laid out using magnetic strips, wires, or optical tracks. These paths ensure precise and repeatable movement patterns, making AGVs ideal for structured environments.
- Tasks: AGVs are primarily used for material handling and transportation tasks. They can move pallets, containers, and other large loads from one point to another within the warehouse, facilitating efficient material flow.
- Benefits: The reliability and accuracy of AGVs in following set routes make them suitable for repetitive, high-volume tasks, reducing labor costs and increasing operational efficiency.
Articulated Arm Robots (AARs)
Function and Capabilities:
- Robotic Arms: AARs are equipped with multi-jointed robotic arms capable of complex movements. These arms can rotate, extend, and bend to pick and place items with high precision.
- Tasks: AARs are ideal for high-volume order fulfillment tasks such as picking individual items from shelves, packing goods into boxes, and sorting products. Their precision and speed make them invaluable in operations requiring detailed handling.
- Benefits: The accuracy and dexterity of AARs enhance productivity and reduce error rates, particularly in tasks that require meticulous handling of small or delicate items.
Autonomous Climbing Robots (ACRs)
Function and Capabilities:
- Vertical Navigation: ACRs are designed to climb vertical surfaces within warehouses, using specialized gripping mechanisms to ascend and descend shelving units.
- Tasks: These robots are particularly useful in high-bay warehouses for inventory management, including tasks like stock checking and retrieving items stored at high elevations.
- Benefits: ACRs maximize vertical storage space and improve inventory accessibility, reducing the need for human workers to use ladders or lifts, thereby enhancing safety.
Mobile Manipulation Robots (MMRs)
Function and Capabilities:
- Combined Mobility and Manipulation: MMRs integrate the mobility of AMRs with the manipulation capabilities of robotic arms. This combination allows them to navigate warehouse environments and perform complex tasks involving the handling and movement of goods.
- Tasks: MMRs can handle a wide range of activities, including picking items from shelves, packing them into boxes, and transporting finished packages to shipping areas. Their versatility makes them suitable for dynamic and varied intralogistics operations.
- Benefits: The multifunctional nature of MMRs offers a flexible solution for warehouses looking to optimize multiple aspects of their operations with a single robotic system.
Each type of intralogistics robot brings unique advantages to warehouse operations, from the flexible navigation of AMRs to the precise handling of AARs and the vertical capabilities of ACRs. By leveraging the strengths of these diverse robotic systems, businesses can significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety in their intralogistics processes, leading to optimized supply chain performance and competitive advantage.
Leading the Charge in Market Growth
As the market for warehouse automation continues to expand, intralogistics robots are at the forefront of this growth. Their capabilities and advantages make them indispensable tools for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chains and improve overall operational efficiency. By leveraging advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and sophisticated sensors, these robots can perform tasks with unmatched accuracy and speed, far exceeding human capabilities in many respects.
Businesses that have adopted intralogistics robots report substantial improvements in productivity, accuracy, and safety. These robots operate tirelessly around the clock, ensuring that warehouse operations continue smoothly and efficiently, even during peak times. The investment in intralogistics robots not only pays off in terms of immediate efficiency gains but also provides a significant long-term return on investment by reducing labor costs and minimizing errors.
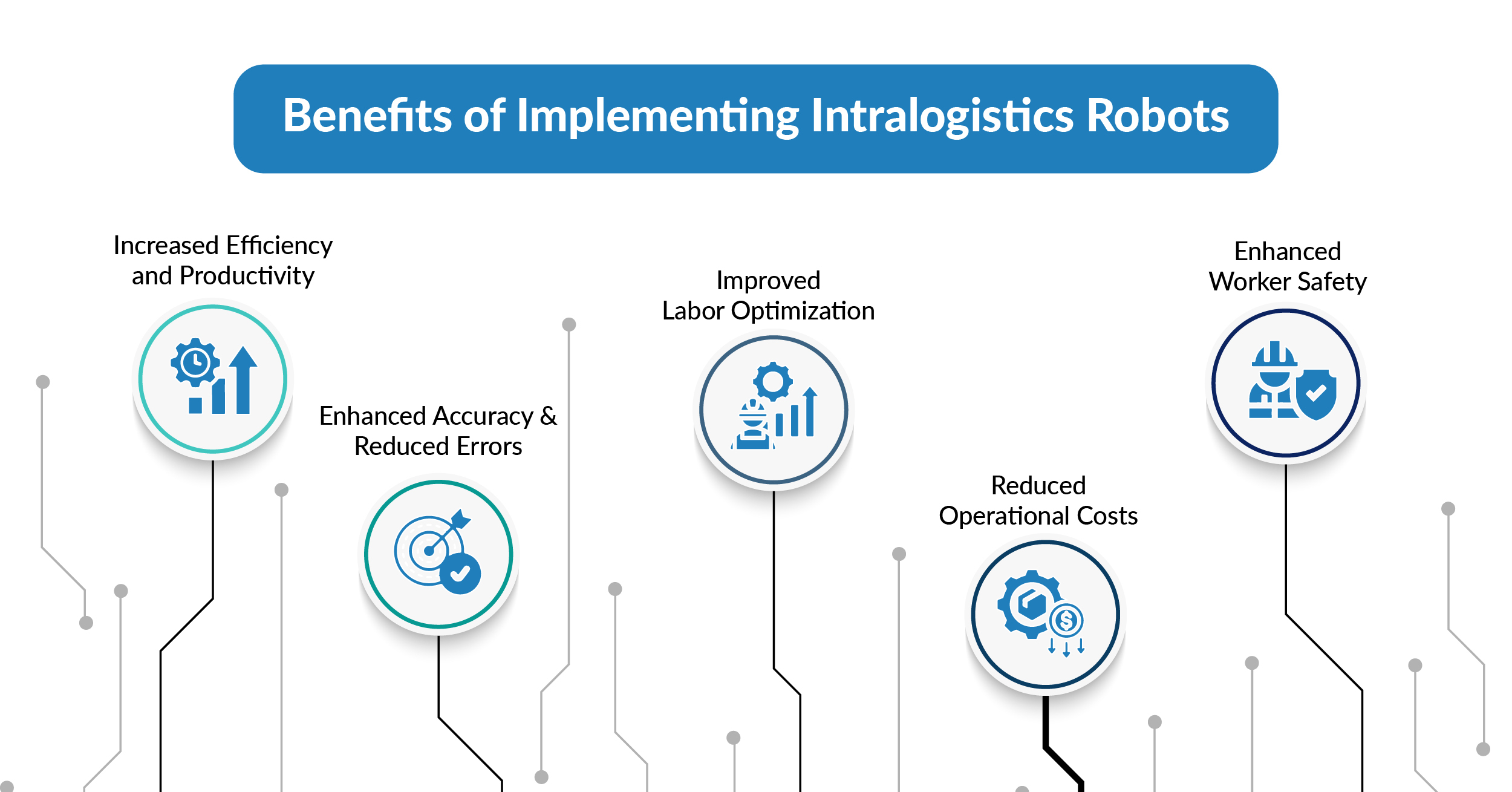
Benefits of Implementing Intralogistics Robots
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Intralogistics robots significantly enhance efficiency and productivity by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows. These robots can operate around the clock without fatigue, handling tasks such as picking, packing, transporting goods, and sorting items with consistent speed and precision. This continuous operation leads to higher throughput, enabling warehouses to process more orders in less time. Additionally, robots can streamline workflows by intelligently managing task assignments and ensuring smooth transitions between different stages of the logistics process. By eliminating bottlenecks and reducing downtime, intralogistics robots contribute to a substantial increase in overall warehouse productivity.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
One of the standout benefits of intralogistics robots is their ability to minimize human error, which is often a significant source of inefficiencies in warehouses. Robots equipped with advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms can perform tasks such as order picking and packing with a high degree of accuracy. They follow precise instructions and consistently handle items correctly, reducing mistakes in order fulfillment. This precision extends to inventory management, where robots can accurately track and update inventory levels in real-time, ensuring accurate stock counts and reducing discrepancies. The result is fewer errors, less rework, and improved customer satisfaction due to accurate and timely deliveries.
Improved Labor Optimization
Intralogistics robots allow human workers to focus on higher-value tasks that require critical thinking, planning, supervision, and quality control. By taking over repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, robots free up human resources for roles that leverage their problem-solving abilities and expertise. This shift not only improves overall job satisfaction for employees but also enhances the operational efficiency of the warehouse. Human workers can oversee robotic operations, handle exceptions, and contribute to continuous improvement initiatives, leading to a more strategic and efficient use of the workforce.
Reduced Operational Costs
The implementation of intralogistics robots can lead to significant cost savings in several areas. First, by automating tasks traditionally performed by human workers, businesses can reduce labor costs and associated expenses, such as overtime and benefits. Second, robots can optimize space utilization within warehouses by efficiently navigating tight spaces and maximizing storage density. This improved space management can defer or eliminate the need for warehouse expansion. Additionally, robots handle items with consistent care, reducing product damage and associated costs. Over time, the reduction in labor costs, improved space utilization, and minimized product damage result in a substantial return on investment for businesses adopting robotic automation.
Enhanced Worker Safety
Safety is a critical concern in warehouse environments, where tasks can often be physically demanding and hazardous. Intralogistics robots can take over dangerous and strenuous tasks, such as lifting heavy objects, working in extreme temperatures, or handling toxic materials. By performing these high-risk activities, robots reduce the likelihood of workplace injuries and accidents. This not only ensures a safer working environment for human employees but also helps businesses avoid costs related to workers’ compensation claims, medical expenses, and lost productivity due to injury-related absences. Enhanced worker safety also contributes to higher morale and retention rates among employees, as they can work in a safer and more comfortable environment.
The benefits of implementing intralogistics robots are multifaceted, encompassing increased efficiency, enhanced accuracy, improved labor optimization, reduced operational costs, and enhanced worker safety. By integrating these advanced robotic systems into their operations, businesses can achieve significant improvements in productivity, cost savings, and overall operational excellence, positioning themselves for long-term success in a competitive market.
Planning and Implementing Intralogistics Robots
Implementing intralogistics robots can transform warehouse operations, but careful planning and execution are essential to realize their full potential. Here’s a practical guide for businesses considering the integration of intralogistics robots.
Identifying Needs and Applications
The first step in implementing intralogistics robots is to evaluate your warehouse needs and identify suitable tasks for automation. Begin by conducting a thorough analysis of current operations to pinpoint areas where inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or high error rates exist. Common tasks that benefit from automation include order picking, packing, transporting goods, and inventory management. By identifying these areas, you can determine where robots will have the most significant impact on productivity and accuracy.
Warehouse Infrastructure Assessment
Assessing your warehouse infrastructure is crucial before deploying intralogistics robots. Evaluate the layout of your facility to ensure it can accommodate robotic operations. This includes considering aisle widths, storage configurations, and potential obstacles. You may need to make modifications to optimize the environment for robotic movement, such as redesigning storage areas or installing markers for navigation. Additionally, check for compatibility with robotic systems, ensuring your warehouse can support the required technology and infrastructure, like Wi-Fi coverage and charging stations for robots.
Selecting the Right Robot Type
Choosing the appropriate type of intralogistics robot is essential for maximizing efficiency. Factors to consider include the specific tasks the robots will perform, the nature of your inventory, and the layout of your warehouse. For instance, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are ideal for dynamic environments where flexibility is needed, while Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are suitable for structured environments with fixed paths. Consider the payload capacity, navigation technology, and integration capabilities of each robot type to ensure they meet your operational requirements.
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration of robots with your existing Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) is vital for efficient operations and lean manufacturing. Ensure that the robots can communicate effectively with your WMS to enable real-time data exchange and synchronization. This integration allows for streamlined task assignments, inventory updates, and workflow management. Collaborate with your WMS provider and robot manufacturer to establish integration protocols and ensure compatibility.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis is critical before committing to intralogistics robot implementation. Calculate the potential return on investment (ROI) by comparing the upfront costs of purchasing and deploying robots against the expected savings from reduced labor costs, increased productivity, and minimized errors. Factor in ongoing maintenance and operational expenses. A thorough cost-benefit analysis will help you make informed decisions and justify the investment to stakeholders.
Safety Training and Risk Assessment
Employee safety is paramount when introducing robots into the workplace. Provide comprehensive training to your staff on safely interacting with robots, including understanding robot capabilities, recognizing safety features, and responding to potential issues. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify and mitigate any hazards associated with robotic operations. Implement safety protocols, such as designated robot zones and emergency stop mechanisms, to ensure a safe working environment for both robots and humans.
Implementing intralogistics robots requires careful planning, assessment, and execution. By identifying your needs, assessing your infrastructure, selecting the right robots, integrating with existing systems, conducting a cost-benefit analysis, and ensuring safety through training and risk assessment, you can successfully leverage robotic automation to enhance your warehouse operations.
The Future of Intralogistics Robots
The field of intralogistics robots is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and emerging trends that promise to further revolutionize warehouse and distribution center operations. Here, we explore key trends shaping the future of intralogistics robots.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to play a pivotal role in the next generation of intralogistics robots. AI advancements enable robots to perform more complex decision-making and task learning, increasing their adaptability and efficiency. With AI, robots can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize routes, predict maintenance needs, and improve task scheduling dynamically. Machine learning algorithms allow robots to learn from past experiences, enhancing their ability to handle unexpected situations and make real-time adjustments. This intelligence empowers robots to operate more autonomously, reducing the need for human intervention and significantly boosting operational efficiency.
Enhanced Human-Robot Collaboration
As technology advances, the interaction between robots and human workers is becoming more seamless and natural. Enhanced human-robot collaboration is a key trend, with robots designed to work alongside humans in shared spaces safely. Advanced sensor technology and AI enable robots to detect and respond to human presence, avoiding collisions and facilitating smooth teamwork. This collaboration allows human workers to focus on complex, value-added tasks while robots handle repetitive, labor-intensive activities. The result is a more efficient and productive workforce, where humans and robots complement each other’s strengths.
The Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work directly with human workers, enhancing productivity and safety in the workplace. In the context of intralogistics, cobots can integrate with traditional intralogistics robots to create a comprehensive automation solution. Cobots are equipped with advanced safety features, such as force-limiting sensors, that allow them to operate safely alongside humans without the need for extensive safety barriers. This integration can lead to more flexible and adaptive operations, where cobots assist with tasks like packing, quality inspection, and assembly, further optimizing the supply chain.
Cloud-based Robotics Management
The potential of cloud-based management and data analysis is transforming how intralogistics robots are monitored and optimized across facilities. Cloud-based systems enable centralized control and real-time monitoring of robot fleets, providing insights into performance metrics and operational efficiency. Data collected from robots can be analyzed in the cloud to identify patterns, optimize workflows, and predict maintenance needs, ensuring minimal downtime. This approach allows businesses to scale their robotic operations efficiently, managing multiple facilities from a single platform and continuously improving robot performance through data-driven insights.
The future of intralogistics robots is being shaped by advancements in AI, enhanced human-robot collaboration, the rise of cobots, and the adoption of cloud-based robotics management. These trends promise to deliver more intelligent, adaptable, and integrated robotic solutions, driving significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and safety within warehouse and distribution center operations. As these technologies continue to develop, businesses that embrace these innovations will be well-positioned to lead in the competitive landscape of intralogistics.
See how Delhivery is revolutionizing logistics with Intralogistics Robots