The Rise of Robots in the Automotive Industry
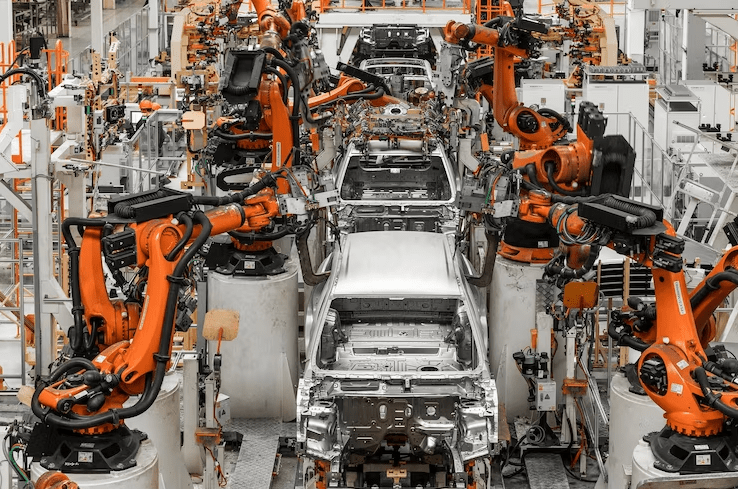
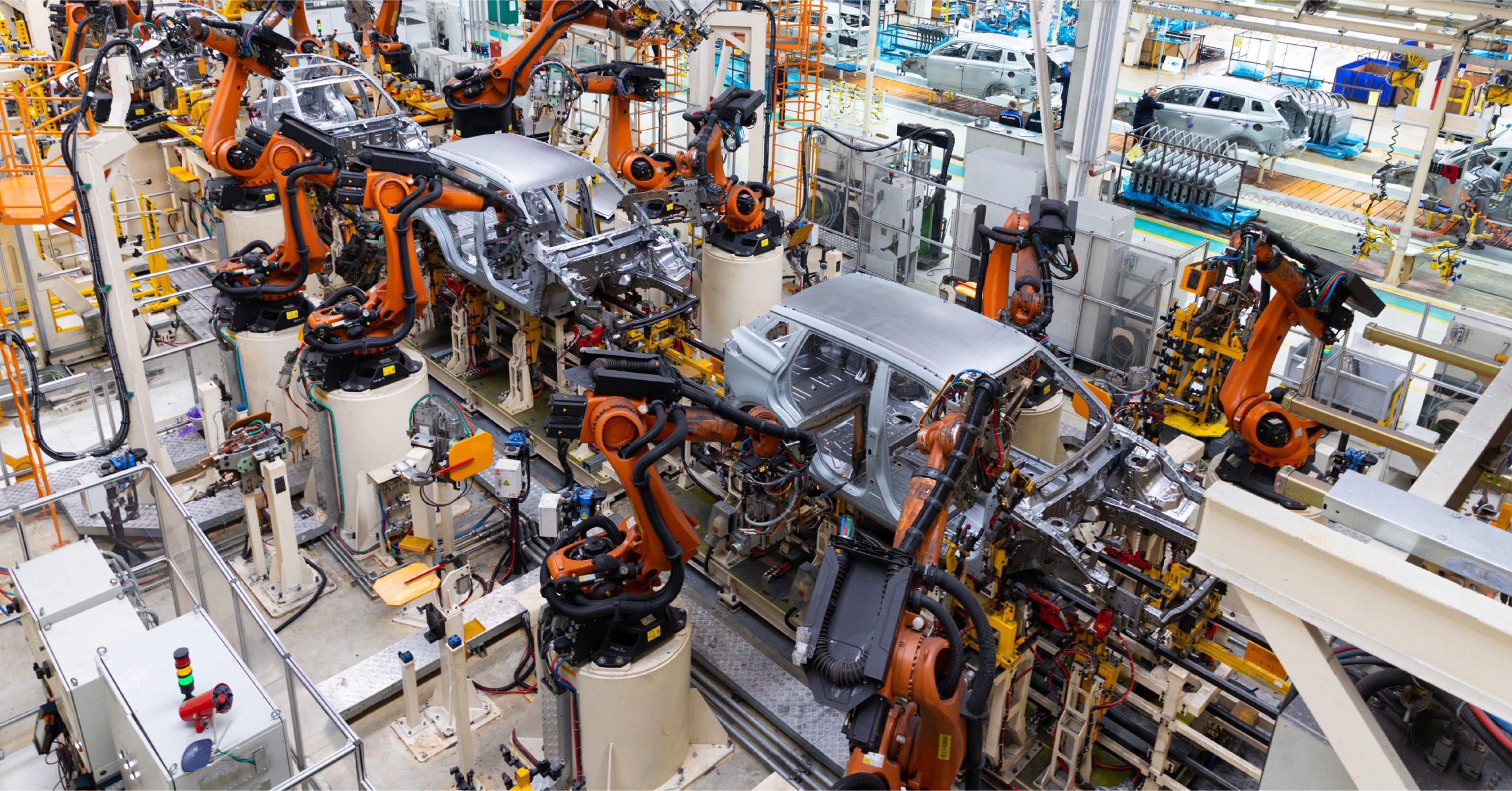
The automotive industry has been at the forefront of technological advancements for decades, with one of the most significant being the adoption of robots. Starting in the 1960s, General Motors introduced the first industrial robot, the Unimate, into their production line. This was a revolutionary moment, marking the beginning of automotive automation in the car manufacturing process. Over the years, robots have evolved from performing simple repetitive tasks to executing complex, precise operations that are essential in modern car production. Today, nearly every aspect of automotive manufacturing involves some level of automation, from assembling components to quality checks.
In recent decades, the automotive industry has increasingly turned to robots to keep pace with the growing demand for high-quality, affordable, and safe vehicles. Robots are now ubiquitous in automotive factories, performing tasks that were once solely carried out by human workers. The introduction of robotics has brought about a paradigm shift in manufacturing, allowing for faster production times, improved accuracy, and enhanced safety.
Several factors have driven this rapid adoption of robots in car production. Labour costs remain one of the primary considerations, especially in regions where wages are high. Robots can work around the clock without fatigue, reducing the need for human labour in many stages of the production process. Efficiency is another key factor. Robots can perform tasks at a speed and precision that humans may find difficult to match, and they are consistent in their work, which leads to fewer errors and defects. Safety is also a major consideration. Robots can take over dangerous and physically demanding tasks, reducing the risk of injuries on the factory floor.
As technology continues to advance, the role of robots in automotive manufacturing will only grow more prominent.
What Robots Can Do in a Car Factory
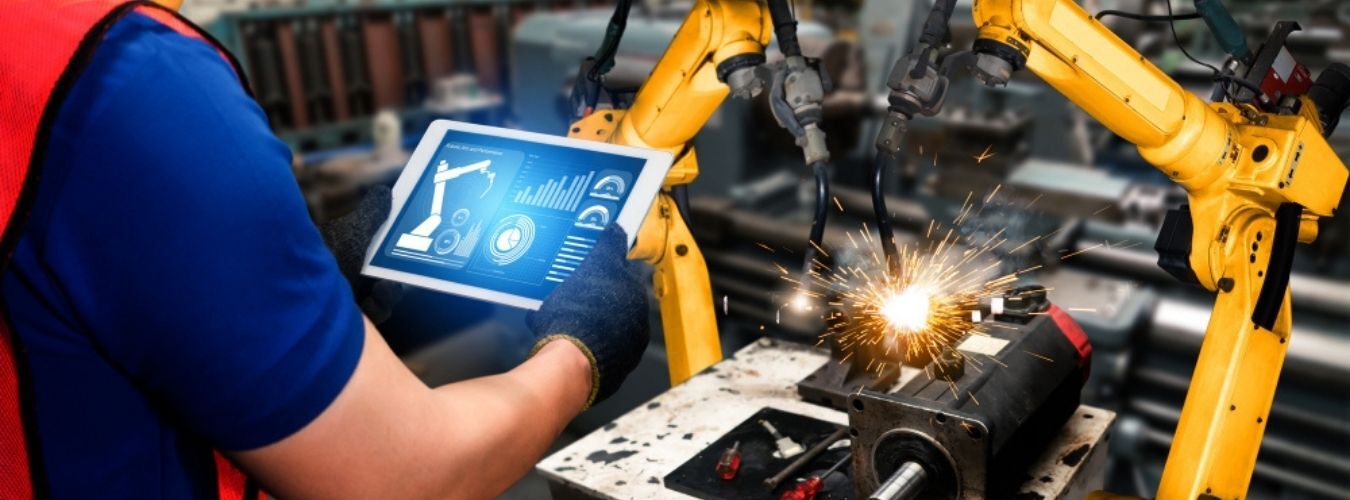
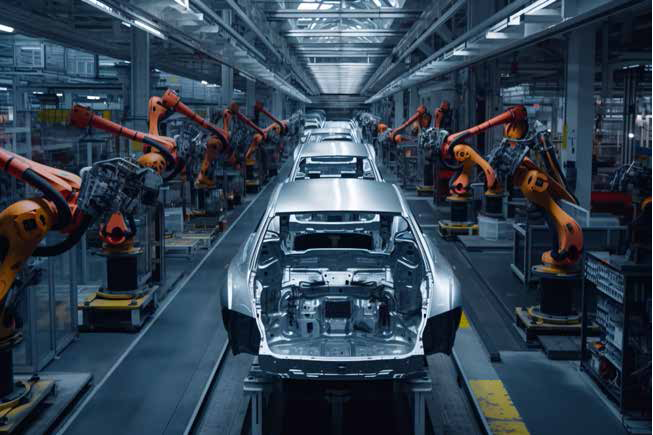
In modern automotive manufacturing, robots handle a variety of tasks across different stages of production. One of the most well-known applications is in the welding process, particularly spot welding, where robots precisely weld parts of a car’s body. This task requires a high degree of accuracy, which robots provide, ensuring strong and reliable welds in a fraction of the time it would take a human worker.
Robots are also heavily involved in painting cars. This is a complex task that requires consistency and precision, especially when applying multiple layers of paint. With robots, car manufacturers can achieve a flawless finish while minimizing waste. Moreover, robots perform tasks like material handling, assembling small components, and conducting quality checks. For example, robots equipped with vision systems can detect defects in car parts, ensuring that only high-quality components are used in production.
The benefits of using robots are clear. They enhance production speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Robots can work 24/7, maintain a consistent performance level, and produce parts with a high degree of precision, reducing the likelihood of defects. However, this doesn’t mean that robots replace humans entirely. In many cases, robots and humans work together, with robots handling repetitive or dangerous tasks while human workers focus on more complex, decision-making roles. This collaboration ensures a productive and safe work environment where both robots and humans complement each other’s strengths.
This rise in automotive automation signals the ongoing transformation of the industry, with robots playing an increasingly critical role in meeting the demands of modern car production.
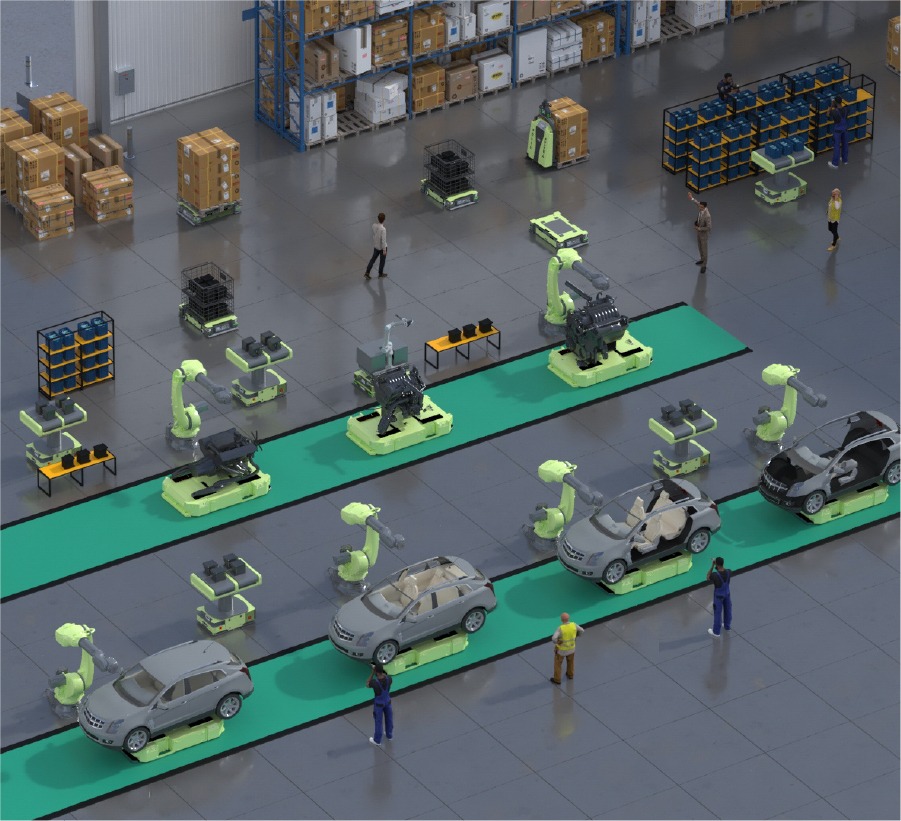
Use of robots in automotive manufacturing is not limited to one type or application. Different categories of robots serve specific functions throughout the car production process. From material handling to assembly and quality inspection, each type of robot plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and precision. Below, we’ll categorize these robots based on their function and the tasks they perform.
Discover how Automotive Automation transforms production efficiency.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
Categorizing Robots by Function
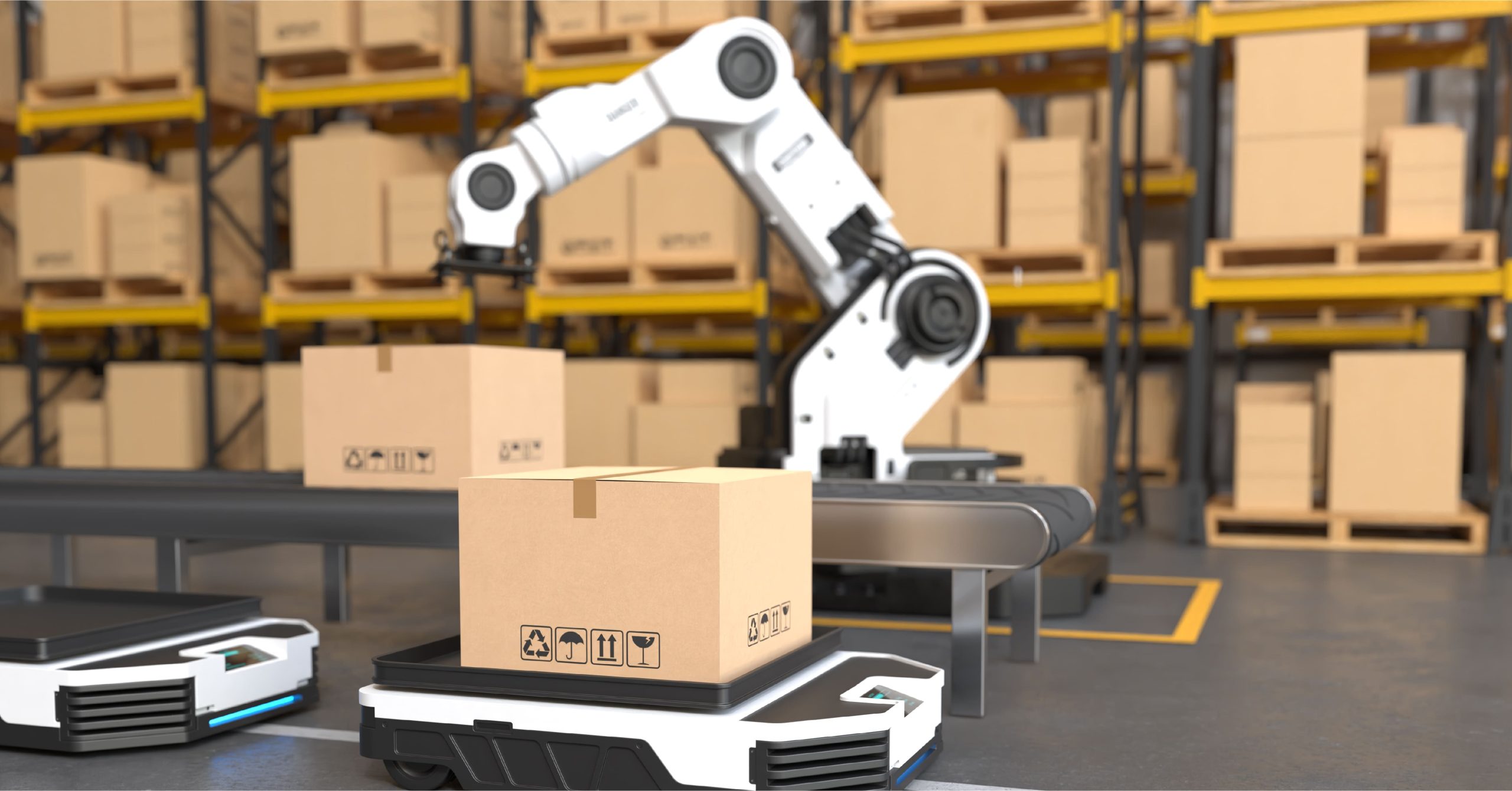
Material handling is one of the most essential functions in automotive manufacturing. Robots designed for material handling can pick up, move, and place parts with high precision and consistency, freeing up human workers from repetitive and physically demanding tasks. Here are some types of robots used for material handling:
- Cartesian Gantry Robots: Cartesian Gantry robots operate along three linear axes (X, Y, Z), making them ideal for pick-and-place tasks that require precision over a large working area. In automotive manufacturing, they are often used for applications such as loading and unloading parts onto conveyor belts or machines. Cartesian robots excel in tasks where high accuracy and repeatability are critical, such as positioning engine parts for assembly.
- SCARA Robots: SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robots are highly efficient for repetitive tasks with short pick-and-place cycles. Their selective compliance allows them to move quickly in the horizontal plane while being rigid in the vertical axis, making them suitable for tasks like assembling small automotive components or loading materials onto conveyor belts.
- Polar Robots: Polar robots have a rotating base and a combination of linear and rotational joints, providing a wide range of motion. This flexibility makes them ideal for tasks like machine loading and unloading or handling materials from overhead. Polar robots are often used in automotive manufacturing to transfer large or irregularly shaped parts that need to be moved across different areas of the factory.
- Delta Robots: Delta robots are known for their high-speed and high-precision capabilities, making them perfect for intricate material handling tasks such as assembling small parts or placing electronic components. Their unique design allows them to move quickly in three-dimensional space, making them ideal for precision tasks where speed is also crucial.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) represent the next generation of material handling robots in automotive manufacturing. Unlike traditional robots, AMRs can navigate through the factory floor without fixed paths, providing flexibility for material transport. AMRs use sensors, cameras, and sophisticated software to move materials between different stages of production, adapting to real-time changes on the shop floor. This flexibility enhances factory logistics, reducing bottlenecks and streamlining the flow of materials.
Robots by Task
2. Welding Robots:
Welding is a critical task in automotive manufacturing, particularly for assembling the car body and chassis. Welding robots are commonly used for both spot and arc welding, delivering speed and precision that is difficult for human workers to match. Here are some types of welding robots used in the industry:
- Articulated Robots: Articulated robots, with multiple rotary joints, offer a versatile range of motion, making them suitable for various welding applications. In automotive manufacturing, articulated robots are frequently used for spot welding, which involves joining two or more metal pieces together at a specific point. These robots provide the accuracy and strength needed to ensure that the welds are strong and consistent, especially when working with the car’s body frame. Arc welding, which requires continuous motion along a seam, is another task handled efficiently by articulated robots.
- Cobots (Collaborative Robots): Cobots are designed to work safely alongside human workers. In automotive manufacturing, cobots are often used for tasks like seam welding, where human oversight may be needed for quality control. Cobots can sense their environment and adjust their speed or force to ensure safety when working in close proximity to humans. Their ability to collaborate with workers makes them a valuable asset in welding tasks that require human intervention or supervision.
3. Painting Robots:
Painting is another critical task in automotive production, where consistency and precision are paramount. Robots are widely used in car painting to ensure even application of paint, reduce waste, and maintain a flawless finish.
- Articulated Robots: Similar to their role in welding, articulated robots are commonly used for painting in automotive factories. Equipped with sophisticated spraying technology, these robots can paint the exterior of cars with high precision, ensuring a consistent application across the entire surface. The ability of articulated robots to reach various angles and areas of the vehicle allows for a more efficient painting process, reducing the time and material waste associated with manual painting.
4. Machine Tending Robots:
Machine tending involves loading and unloading materials into machines such as CNC machines, which are commonly used in automotive manufacturing. Robots used for machine tending help improve efficiency by minimizing downtime and ensuring a continuous flow of materials.
- Cartesian Gantry Robots: Cartesian Gantry robots excel at precision tasks like machine tending, where accuracy and consistency are crucial. These robots can precisely load raw materials into machines and unload finished products, ensuring smooth operation. In the automotive industry, they are often used to load parts into CNC machines for machining or shaping, ensuring that production continues without interruption.
- SCARA Robots: SCARA robots are well-suited for fast and repetitive machine tending tasks, particularly in environments where speed is essential. Their quick, efficient motion allows them to handle the loading and unloading of materials from machines at a rapid pace, reducing cycle times and increasing productivity on the factory floor.
5. Assembly Robots:
Assembly is a core function in automotive manufacturing, from installing engines and transmissions to assembling interior components. Robots play a vital role in ensuring precision and speed in this process.
- Articulated Robots: Articulated robots are widely used for complex assembly tasks in automotive manufacturing. Their flexibility and dexterity make them ideal for installing large components like engines or attaching smaller parts to the vehicle’s body. These robots can perform multiple tasks in a single motion, such as tightening bolts, installing dashboards, or attaching doors, improving overall production efficiency.
- SCARA Robots: SCARA robots are effective in high-speed assembly tasks, especially when dealing with smaller components. Their ability to work quickly and accurately makes them suitable for assembling parts like electronic components, fasteners, and other small pieces that are essential in car manufacturing.
- Cobots: Cobots are increasingly used in assembly processes where human-robot collaboration is necessary. For example, cobots can work alongside human operators to install interior features or handle delicate components. Their safety features and ease of programming make them ideal for collaborative assembly tasks, where precision and teamwork are key.
6. Quality Inspection Robots:
Ensuring the quality of each part and final vehicle is crucial in automotive manufacturing. Robots equipped with advanced vision systems can perform automated inspections to ensure that each product meets the required standards.
- Vision-equipped Robots: Quality inspection robots use cameras and sensors to detect defects in parts and finished products. These robots can be programmed to inspect welds, measure dimensions, and verify the accuracy of assemblies. In automotive manufacturing, robots with vision systems ensure that only high-quality parts make it through the production process, reducing the risk of recalls and ensuring customer satisfaction.
The use of robots in automotive manufacturing continues to expand, with each type of robot designed to handle specific tasks that improve efficiency, safety, and quality. From welding to painting, material handling to quality inspection, robots have transformed the automotive industry, making production faster, safer, and more reliable. As technology advances, the role of robots will only grow, driving innovation in car manufacturing for years to come.