Distracted Driving
Understanding Distracted Driving
Importance of driver focus and awareness for road safety
Explore how ADAS technology can help you overcome dangerous distracted driving habits.
Download our Brochure/E-book for expert insights.
Categories of distracted driving
Distracted driving can be broken down into three main categories, each of which presents its own unique challenges and risks on the road: visual distractions, manual distractions, and cognitive distractions.
- Visual Distractions: Visual distractions occur when a driver’s eyes are taken off the road, diverting their attention away from potential hazards and impairing their ability to react quickly to changing circumstances. Common examples of visual distractions include:
-
- Using smartphones: Whether texting, browsing the internet, or checking social media, using smartphones while driving is one of the most prevalent and dangerous forms of visual distraction.
- Adjusting navigation systems: Fiddling with GPS devices or map apps to input destinations or adjust routes can lead to momentary lapses in attention and increase the risk of accidents.
- Viewing roadside billboards or scenery: While visually appealing, billboards and scenic views can draw a driver’s eyes away from the road, especially if they linger on them for too long.
- Manual Distractions: Manual distractions involve activities that require a driver to take their hands off the steering wheel, compromising their ability to maintain control of the vehicle. These distractions include:
-
- Eating or drinking: Consuming food or beverages while driving may seem harmless, but it can result in spills, sudden movements, and reduced reaction times.
- Applying makeup or grooming: Personal grooming activities such as applying makeup, shaving, or fixing hair divert a driver’s attention and increase the risk of accidents.
- Reaching for objects: Retrieving items from the backseat, dashboard, or floor of the vehicle can cause a driver to momentarily lose focus on the road ahead.
- Cognitive Distractions: Cognitive distractions occur when a driver’s mind wanders away from the task of driving, impairing their ability to process information and make quick, accurate decisions. Examples of cognitive distractions include:
-
- Daydreaming: Allowing the mind to wander or engage in unrelated thoughts while driving can significantly reduce a driver’s awareness of their surroundings.
- Worrying or stressing: Emotional distractions such as worrying about work, finances, or personal relationships can preoccupy a driver’s mind and interfere with their ability to concentrate on the road.
- Engaging in loud conversations: Conversations with passengers, particularly those that are emotionally charged or require deep concentration, can distract a driver’s attention from the road ahead.
By understanding the three main categories of distracted driving and the activities that fall within each, drivers can take proactive steps to minimize distractions and prioritize safety on the road. Whether it’s putting away electronic devices, avoiding multitasking, or practicing mindfulness while driving, every effort to stay focused behind the wheel contributes to safer roads for all.
Dangers of distracted driving
Distracted driving poses significant dangers on the road, with potentially devastating consequences for drivers, passengers, and pedestrians alike. By diverting attention away from the task of driving, distractions impair a driver’s ability to react quickly and effectively to changing road conditions, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries. Here’s how distracted driving undermines road safety and why it can be as dangerous as drunk driving:
- Slowed Reaction Times: When drivers are distracted, their ability to perceive and respond to hazards is compromised. Research has shown that engaging in distractions can significantly slow reaction times, making it more difficult for drivers to brake, steer, or take evasive action in critical situations. Even a split-second delay in reaction time can have serious consequences, especially when traveling at high speeds or in congested traffic.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Distracted driving dramatically increases the likelihood of accidents on the road. Whether it’s texting behind the wheel, adjusting the radio, or engaging in a conversation, any activity that takes a driver’s attention away from driving significantly raises the risk of collisions. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), distracted driving contributes to thousands of fatalities and hundreds of thousands of injuries each year in the United States alone, making it one of the leading causes of traffic accidents.
- Comparable Danger to Drunk Driving: The dangers of distracted driving are often compared to those of drunk driving, and for good reason. Both behaviors impair a driver’s ability to operate a vehicle safely, leading to impaired judgment, reduced coordination, and increased risk-taking behavior. Studies have shown that texting while driving, for example, can be as dangerous as driving with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.08%, the legal limit in many jurisdictions. In fact, research from the National Safety Council (NSC) suggests that texting behind the wheel is six times more likely to cause an accident than driving while intoxicated.
Ultimately, the consequences of distracted driving are far-reaching and can have lifelong impacts on individuals and communities. From minor fender-benders to catastrophic collisions resulting in fatalities, the risks associated with distracted driving are simply not worth taking. By recognizing the dangers and committing to staying focused and attentive behind the wheel, drivers can help prevent accidents and make our roads safer for everyone.
Consequences of distracted driving
The consequences of distracted driving accidents are far-reaching and extend beyond the immediate incident, impacting individuals, families, and communities in profound ways.
- Loss of life and serious injuries: Distracted driving accidents often result in the loss of life or cause serious injuries that can have lifelong implications for victims and their families. Lives are irrevocably changed in an instant, leaving behind grieving families and shattered communities. The emotional toll of losing a loved one or coping with severe injuries is immeasurable and can have lasting effects on mental health and well-being.
- Economic costs: Distracted driving accidents impose significant economic burdens on individuals, families, and society as a whole. Medical costs associated with treating injuries, rehabilitation expenses, and long-term care can quickly accumulate, placing financial strain on victims and their families. Additionally, property damage resulting from accidents, including vehicle repairs or replacement, adds to the financial burden. Moreover, accidents can lead to lost productivity due to injuries or fatalities, impacting employers and the economy at large.
- Emotional trauma: The emotional trauma of distracted driving accidents is profound and enduring, affecting not only victims and their families but also witnesses and first responders. Survivors may experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, depression, and other psychological effects following the trauma of an accident. Families are left to grapple with grief, guilt, and profound loss, while witnesses may suffer from survivor’s guilt or trauma from witnessing the accident unfold.
Furthermore, the ripple effects of distracted driving accidents are felt throughout communities, as neighbors, friends, and coworkers are impacted by the loss of life or injuries. The emotional scars left behind can linger for years, serving as a poignant reminder of the devastating consequences of distracted driving.
Legal consequences of distracted driving
In many regions, distracted driving carries serious legal consequences aimed at deterring this dangerous behavior and promoting road safety. Penalties for distracted driving can vary depending on local laws and regulations but commonly include:
- Fines: Drivers caught engaging in distractions such as texting or using handheld devices while driving may face hefty fines, which can range from moderate to substantial amounts depending on the jurisdiction.
- License Points: In some regions, distracted driving violations result in the accumulation of demerit points on the driver’s license. These points can lead to license suspension or revocation if they exceed a certain threshold within a specified timeframe.
- License Suspension: Repeat offenders or drivers involved in severe distracted driving incidents may face temporary or even permanent suspension of their driver’s license. This penalty serves as a deterrent and ensures that unsafe drivers are taken off the road until they demonstrate a commitment to safe driving practices.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: Convictions for distracted driving can lead to significant increases in auto insurance premiums, as insurers consider such drivers to be at higher risk of accidents and claims.
- Criminal Charges: In cases where distracted driving results in serious injury or death, drivers may face criminal charges such as vehicular manslaughter or reckless driving, which carry severe penalties including imprisonment.
By imposing strict legal consequences for distracted driving, authorities aim to discourage this risky behavior and protect the safety of all road users. However, it’s important to note that the legal framework surrounding distracted driving may vary from one jurisdiction to another, so drivers should familiarize themselves with the specific laws and penalties applicable in their area to avoid legal repercussions.
Common Distracted Driving Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Practical tips and strategies for drivers to stay focused and avoid distractions:
- Plan your trip:
- Map out your route in advance and set your navigation system before you start driving.
- Minimize the need to use your phone while driving by planning your route and destination ahead of time.
- Eliminate distractions from your car:
- Put your phone away in a location out of reach, such as the glove compartment or backseat.
- Silence notifications and alerts to avoid the temptation of checking your phone while driving.
- Avoid eating or drinking while driving to prevent spills and maintain focus on the road.
- Adjust mirrors and controls beforehand:
- Set up your mirrors, climate control, and radio settings before you start driving to minimize the need for adjustments while on the road.
- Let passengers know:
- Inform passengers about the importance of minimizing distractions while you’re driving.
- Encourage passengers to refrain from engaging in distracting behavior, such as loud conversations or playing music at high volumes.
- Take breaks on long journeys:
- Plan rest stops every two hours or as needed to stay alert and avoid fatigue.
- Use rest stops to stretch your legs, refuel, and refresh before continuing your journey.
- Be aware of your surroundings:
- Stay focused on the road ahead and be aware of traffic signals, signs, and other vehicles.
- Avoid daydreaming or zoning out while driving by actively scanning your surroundings and anticipating potential hazards.
- Utilize hands-free technology:
- If you must use your phone while driving, utilize hands-free calling or voice commands for navigation.
- Invest in hands-free devices or Bluetooth technology to minimize distractions and keep your hands on the wheel.
By implementing these practical tips and strategies, drivers can reduce distractions, stay focused on the road, and promote safer driving habits for themselves and others on the road.
Technologies to Combat Distracted Driving
Emerging technologies offer promising solutions to reduce distracted driving and improve road safety:
- In-vehicle phone blocking systems:
- Software solutions are being developed to disable phone use while driving by blocking calls, texts, and app notifications when the vehicle is in motion.
- These systems utilize GPS and motion sensors to detect when the vehicle is moving and automatically activate phone-blocking features.
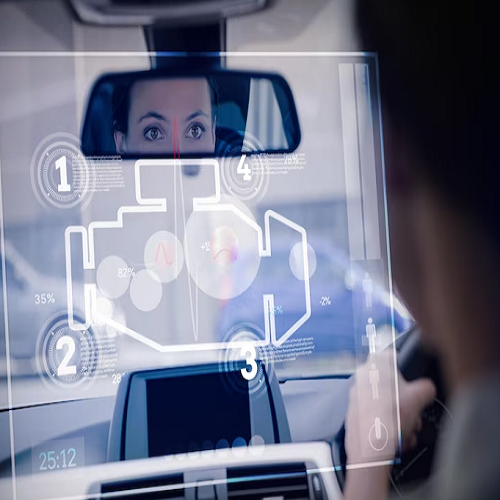
- Driver monitoring systems:
- Camera-based systems can monitor driver behavior in real-time, detecting signs of drowsiness, distraction, or other concerning behaviors.
- By analyzing facial expressions, eye movements, and head position, these systems can alert drivers to potential hazards and encourage them to maintain focus on the road.
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS):
- ADAS features, such as lane departure warning and automatic emergency braking, utilize sensors and cameras to enhance vehicle safety.
- Lane departure warning alerts drivers when they unintentionally drift out of their lane, while automatic emergency braking intervenes to prevent or mitigate collisions with vehicles or pedestrians.
These emerging technologies have the potential to significantly reduce distracted driving and improve overall road safety. By leveraging advancements in software, sensors, and artificial intelligence, manufacturers and developers are pioneering innovative solutions to mitigate the risks associated with distracted driving and create safer driving environments for all road users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the consequences of distracted driving accidents are multifaceted and devastating, encompassing loss of life, serious injuries, economic costs, and emotional trauma. Addressing this pressing issue requires a concerted effort from individuals, communities, policymakers, and stakeholders to promote safe driving habits, raise awareness, and implement measures to prevent distracted driving accidents and protect road users. We encourage readers to learn more about DMS and consider choosing vehicles equipped with this life-saving technology.