There’s no denying the fact that in today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, it is the emergence of smart factories that have thoroughly revolutionised the manufacturing processes. However, it is robotic automation that is the very pulse of this transformation. This robotic automation is a cutting-edge technology that has redefined the traditional way in which factories used to operate. This detailed blog attempts to explore the critical role of Robotic Automation in smart factories, delving further into topics such as Mobile Production Stations (MPS), Intralogistics, Vision Guided Robotic Automation, Augmented Worker, Vision Inspection, and Digital Workflow. So do give this blog a read as implementing robotic automation shall help you scale your business operations.
-
Smart Factory Revolution:
Robotic Automation stands tall at the forefront of the smart factory revolution. It essentially involves the use of automated systems, such as robots and autonomous machinery. These in turn perform tasks that were traditionally handled by human workers. Furthermore, these robots which work round the clock, are equipped with advanced sensors and programming and this helps enhance their overall adaptability, precision, and efficiency.
Smart factories strategically leverage Robotic Automation to streamline their production processes, cut down on the scope for human error, and thereby increase their overall productivity. As a result, industries can now meet growing demands and maintain high-quality standards with ease.
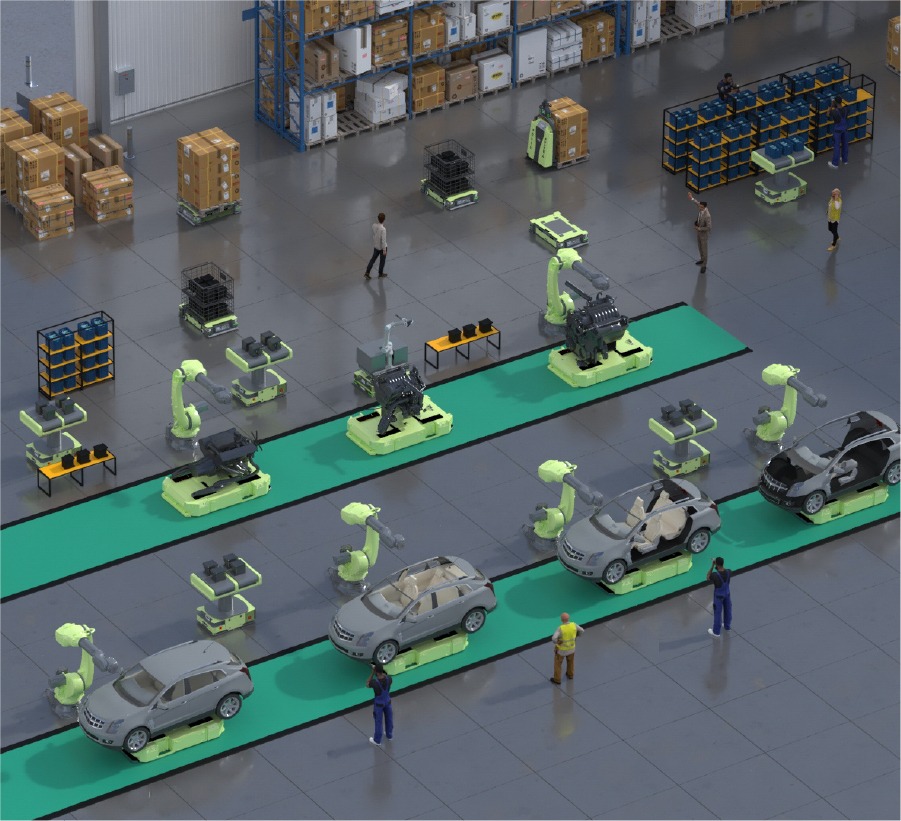
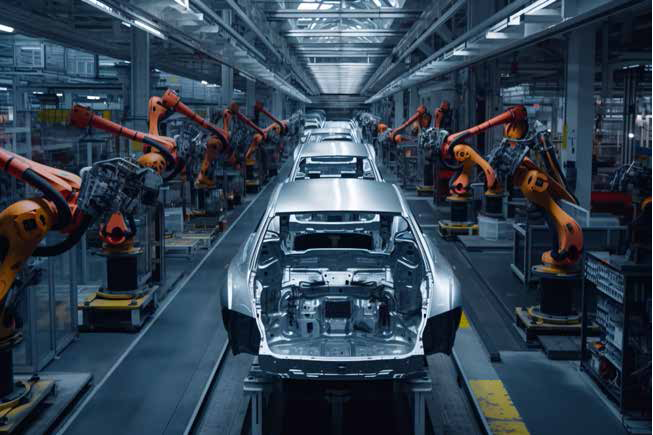
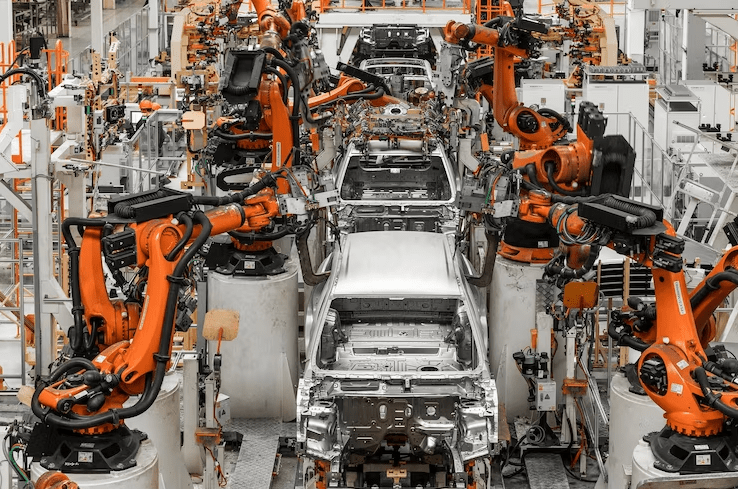
An apropos example of a smart factory is a car manufacturing plant that extensively employs robotic automation.
Here in such factories, robotic arms are made use of in order to assemble the various parts of the car, weld components, and perform the overall quality inspections. These robots in such factories work 24/7, and are completely equipped with advanced sensors. This in turn helps detect any kind of defects or anomalies in the production process.
Such robots, unlike humans, can also quickly adapt to changes while maintaining high levels of precision and efficiency. So car manufacturing plants utilize robotic automation to enhance their productivity while consistently meeting the demand for high-quality cars in the market.
Discover how Robotic Automation powers efficiency in Smart Factories.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
-
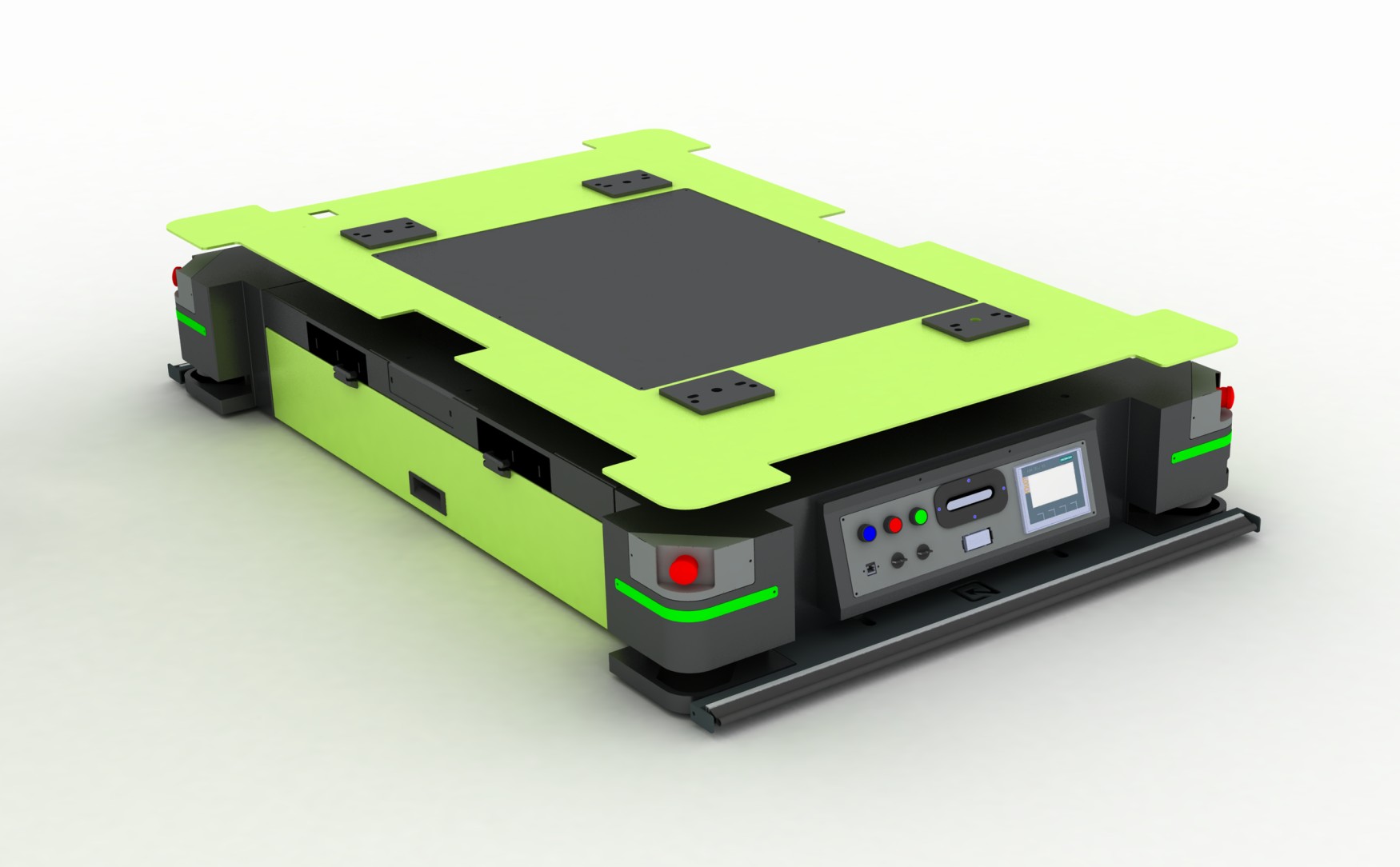
Mobile Production Stations (MPS)
Mobile Production Stations, or MPS, are an integral and indispensable part of the smart factory system. These mobile units equipped with robotic arms can navigate through the factory floor, adjusting their operations as and when required.
Mobile Production Stations are essentially programmed to transport materials from one point to another. In addition to this, MPS also assists in assembly and performs quality checks. This mobility and adaptability that the MPS offer, help enhance the overall efficiency of manufacturing processes.
For those unversed, Mobile Production Stations are autonomous and agile units that can gracefully navigate the factory floor, just like a chess piece moving strategically across a board. Mobile Production Stations are typically not bound within a static location, but they rather move around with precision and purpose, and this facilitates them to adapt to the ever-evolving production demands.
Herein it is important to note that it is the Robotic Automation that actually powers MPS, allowing the mobile production stations to interact with other machinery and personnel while ensuring a seamless workflow within the smart factory system.
The Mobile Production Station units are thus versatile in their capabilities and are programmed to handle a multitude of tasks. They are actually the real workhorses of smart factories as they seamlessly execute a range of operations that help optimize the overall production process. Mentioned below is a quick overview of some use cases of the mobile production station.
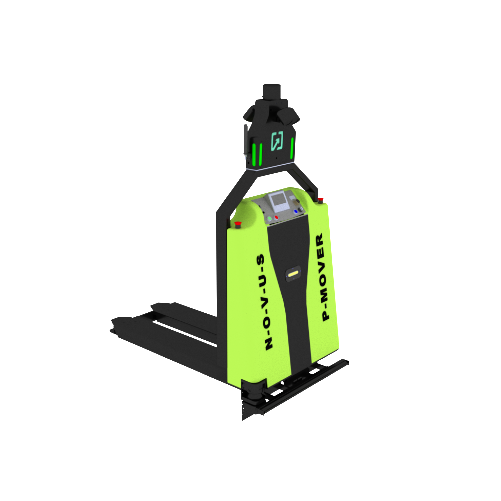
1. Material Transport: MPS units efficiently transport raw materials and components to various assembly points, ensuring an uninterrupted and continuous flow of materials. This eliminates the need for manual material handling and therefore, reduces the scope for any kind of unsolicited errors and delays. Novus P-Mover, Novus Hi-Tech’s Autonomous Battery Operated Pallet Truck are ground-to-ground and ground-to-height material handling experts. You can effortlessly transport standard bins and pallets with pinpoint precision & simplify material handling with our Novus P-Mover.
In the automotive industry, Mobile Production Stations are used to transport car parts to the main assembly line. MPS thus, bring engines, chassis components, and other essential parts to the exact location where they are required for assembly.
2. Assisting in Assembly: Mobile Production Stations are not just responsible for bringing the various components to their assembly location, but well, these mobile production stations also take active participation in the assembly process. With their robotic arms and precision control, they can assist human workers in tasks that require accuracy, repetition, or those performed in constrained spaces.
A real life example of the same would be the use of MPS units in electronics manufacturing. Here the MPS units collaborate with assembly line workers to precisely position delicate microchips on circuit boards. This guarantees a high degree of precision that is otherwise quite a herculean task to achieve manually.
3. Quality Checks: Besides the material transportation and assembly assistance that the Mobile Production Stations offer, these MPS are also equipped with sensors and cameras and they help ensure to a tee quality checks. MPS helps conduct real-time and absolutely scrupulous quality checks during the manufacturing process. This helps identify defects and inconsistencies, which is extremely crucial for maintaining uniform and high-quality standards.
A real-life example of the same is the use of mobile production stations within the food industry. Mobile Production Stations equipped with vision systems thoroughly inspect packaged food products for defects, ensuring that only top-quality items reach the end consumers.
Here it is important to note that at the very nuclei of this flexibility and efficiency offered by MPS units is Robotic Automation, that acts as a catalyst and certainly a powerful enabler. This technology endows the Mobile Production Stations with unparalleled intelligence, precision, and the ability to interact seamlessly with other machinery and human personnel. These robots are not only autonomous but are rather collaborative, creating a harmonious synergy within the smart factory system.
Real-Life Success Story using Mobile Production Stations
Consider a global electronics manufacturer that implemented Mobile Production Stations within its factories. These stations, equipped with robotic arms and vision systems, certainly played a cardinal role in the smooth production of smartphones. They moved from one assembly point to another, seamlessly transporting the various delicate electronic components and assisting human workers in intricate tasks. This in turn helped increase the production efficiency which left a small room for errors and offered an impressive boost in the overall product quality.
Mobile Production Stations therefore represent a paradigm shift in conventional manufacturing, epitomising the agility and adaptability required in the modern industrial landscape. Their overall mobility, versatility, and the fusion of Robotic Automation makes these mobile production stations a linchpin of the smart factories, ensuring that manufacturing processes remain efficient, error-free, and responsive to the ever-evolving market demands.
MPS units are therefore the ultimate catalysts for success, enabling industries to maintain their competitive edge while delivering excellence to their customers.
-
Intralogistics to Streamline Material Handling:
Intralogistics, which is a fundamental component of modern smart factories, revolves around the intricate management of internal logistics within manufacturing facilities. The seamless operation of intralogistics is made possible through the meticulous integration of Robotic Automation, which again plays a key role in augmenting this critical aspect of industrial operations.
However, it is important to mention herein that within the very domain of intralogistics, an array of autonomous robots and guided vehicles take on key responsibilities, including the transport, storage, and retrieval of materials. These robots and vehicles operate in concert with sophisticated integrated systems, such as warehouse management software in order to accomplish their essential objectives. The robots here primarily contribute to a substantial reduction in operational errors, thereby bolstering the overall precision and reliability of internal logistics processes. Furthermore, they also significantly amplify the operational efficiency by ensuring a smooth and timely flow of materials and products.
Novus Carry AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots), redefine material handling, automate material flow & streamline transportation. At Novus Hi-Tech, we provide different variants of AMR depending on the need of your enterprise based on factors like payload capacity, specific use cases, and the dimensions of your facility, all of which are instrumental in determining the optimal solution for your operations.
This incredible integration of Robotic Automation within intralogistics is certainly instrumental in the precise orchestration of materials and products within the manufacturing plant. This means that resources are efficiently placed wherever they are needed, and precisely when they are required. This meticulous control over material flow, facilitated by advanced robotic technology and intelligent software systems, underlines the crucial role of intralogistics in ensuring the continued productivity and competitiveness of modern manufacturing facilities.
-
Vision Guided Robotic Automation in Smart Factories
Vision Guided Robotic Automation is a game-changer for quality control in manufacturing. Robots equipped with cameras and computer vision technology can identify defects, measure dimensions, and also ensure the overall product quality. These systems provide a level of precision that surpasses human capabilities. Furthermore, by making use of advanced visual recognition and analysis, these robots contribute to the production of high-quality goods, which is indeed a cornerstone of smart factories. Here are some examples to further elaborate on vision guided robotic automation.
1. Defect Detection : Imagine a car manufacturing plant where robots equipped with cameras scan each and every vehicle’s body to detect defects such as scratches, dents, or paint imperfections. So if a flaw is detected, then the robot can immediately signal for corrective action to be taken, ensuring that only pristine cars make it to the market.
2. Dimensional Accuracy : In the electronics industry, robots equipped with vision systems can accurately measure tiny components with incredible and absolutely unparalleled precision. For instance, in smartphone production, these robots can verify the exact placement and alignment of the various minuscule components, ensuring that each device meets strict dimensional specifications.
3. Customization : In the fashion industry, robots with vision technology can help scan and analyze customer body measurements for tailored clothing with fine customer experience. This allows for precise customizations, ensuring a perfect fit for each individual, while also enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Smart Factories : Vision-guided robotic systems play a pivotal role in smart factories. They essentially help in maintaining consistently high product quality. For example, in a semiconductor manufacturing plant, robots equipped with vision systems can check for microscopic defects in silicon wafers, ensuring that only the finest quality wafers are used in the final chip production process.
5. Quality Assurance in Food Processing : In the food industry, vision-guided robots can be used to keep an eagle’s eye and inspect products such as fruits. These robots can identify blemishes, size, and even the ripeness, ensuring that only high-quality fruits are selected for packaging. This not just enhances the customer experience but also prevents food wastage.
-
Augmented Worker
The concept of the “Augmented Worker” in the context of Collaborative Robotics is centered on the idea of Robotic Automation. This essentially complements and enhances the overall capabilities of human workers rather than completely substituting them. This approach emphasises the symbiotic relationship between humans and robots in the workplace.
Here it is interesting to note that such collaborative robots are commonly referred to as “cobots,” and these are integral to this paradigm. Cobots are designed to work in close proximity to human operators and this therefore creates a harmonious environment where both humans and machines mutually share their tasks and responsibilities. These robots are specifically engineered to assist with tasks that are repetitive, physically strenuous, or potentially hazardous. Such cobots thus contribute to the improvement of workplace safety and overall productivity.
In the context of the smart factory, the integration of the Augmented Worker concept signifies an all new age of industrial synergy. In this setting, human workers and robots collaborate seamlessly, harnessing the creative problem-solving abilities of human intelligence and combining them with the precision and swiftness of automation. This collaborative effort results in a highly efficient and productive workforce, where the strengths of both humans and robots are leveraged to create a more innovative and competitive manufacturing environment.
-
Vision Inspection :
Vision Inspection systems are a crucial element of quality control in smart factories. These systems use cameras and artificial intelligence to scrutinise products for defects or inconsistencies. The immediate feedback they provide allows for rapid adjustments to manufacturing processes, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Robotic Automation is instrumental in these systems, ensuring the swift and accurate inspection of products.
-
Digital Workflow :
The seamless integration of digital workflows is a cornerstone of smart factories, and at its very core lies Robotic Automation, which serves as the linchpin that connects and synchronises the various elements within the factory environment. This integration isn’t merely about automating tasks; it’s a profound transformation of how the factory operates, improving efficiency and data management.
Robotic Automation acts as a bridge, facilitating the exchange of data and information between different entities in the manufacturing ecosystem. This includes the machinery and equipment on the factory floor, the overarching systems that govern production, and the human workforce. By establishing these interconnected pathways, the factory becomes a dynamic and adaptive environment where data flows seamlessly, fostering a new level of operational synergy.
One of the most notable advantages of this integration is the enhancement of decision-making processes. The real-time exchange of data and insights enables the factory to respond to changing conditions with agility. It allows for swift adjustments and optimizations in production processes, ensuring that the factory can adapt to market demands, minimize downtime, and optimize resource utilization. In essence, this interconnectedness empowers the factory with the ability to make more informed decisions, reduce errors, and maximize overall efficiency.
The result is a smart factory that is not only highly productive but also agile and responsive. It aligns with the modern industrial landscape, where adaptability, data-driven insights, and streamlined workflows are critical for maintaining competitiveness and ensuring the efficient use of resources.
In conclusion, Robotic Automation plays an indispensable role in the transformation of traditional factories into smart factories. From Mobile Production Stations and Intralogistics to Vision Guided Robotic Automation, Augmented Worker, Vision Inspection, and Digital Workflow, the impact of Robotic Automation is pervasive and transformative. Manufacturers who embrace this technology are better equipped to meet the demands of the modern market, producing high-quality products efficiently and staying competitive in a rapidly changing industrial landscape.
By harnessing the power of Robotic Automation, smart factories are not only boosting productivity but also opening the door to a future where manufacturing is more efficient, sustainable, and adaptable than ever before. It’s safe to say that Robotic Automation is the cornerstone of the smart factory revolution.
At Novus Hi-Tech, we have helped transform operations for leading manufacturers and revolutionized their assembly line processes for increased efficiency and enhanced productivity through our robotic automation solutions. Get to know how we did the same, here. For more details you can schedule a consultation with our core team to get a live demo of our robotic solutions.