Introduction: Embracing the Robotic Revolution
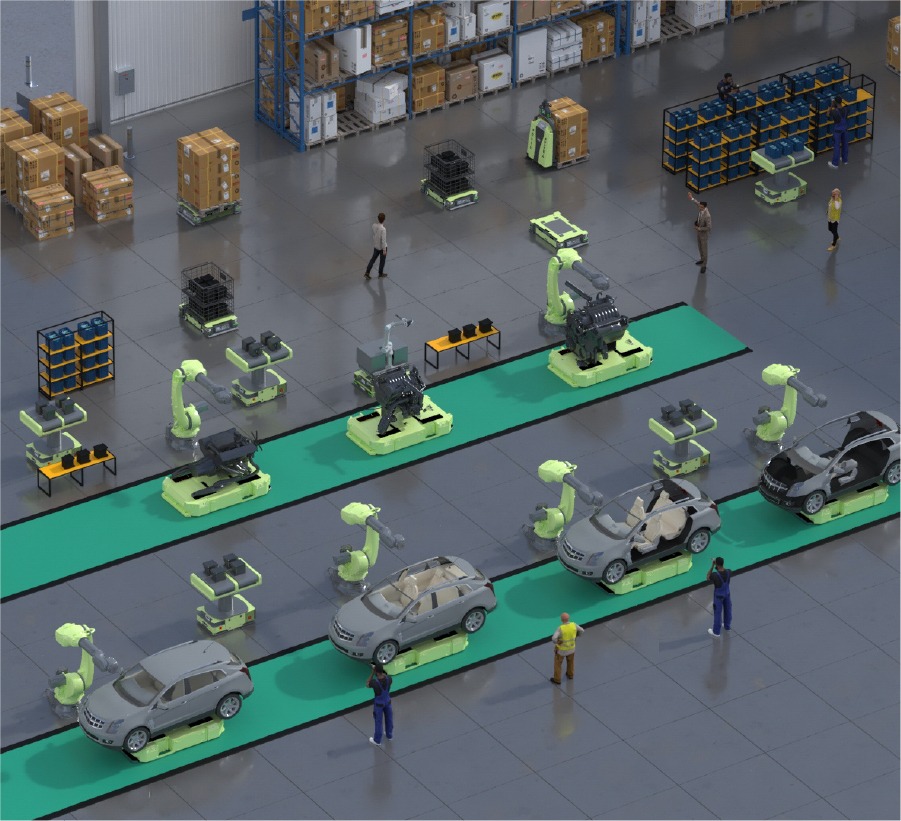
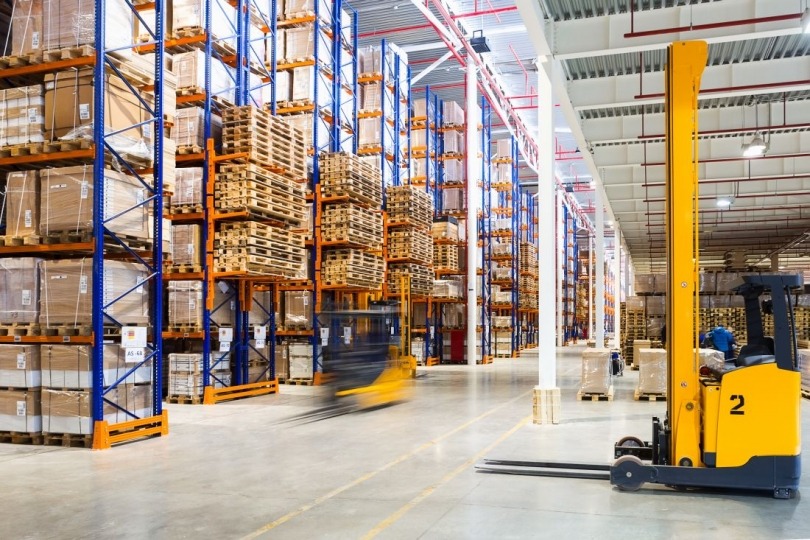
In today’s factories, automated robots Manufacturing have become essential partners, transforming the manufacturing industry. Gone are the days of labor-intensive assembly lines and manual material handling. Today, factories work with the precision of robotic arms, seamlessly performing complex tasks with speed and accuracy. These machines are no longer just tools; they are now crucial for achieving top quality and staying competitive.
Robots in Manufacturing
Automation has ushered in a new era in manufacturing, marked by flexibility, high productivity, and constant innovation. As global markets evolve and consumer demands become more sophisticated, companies must enhance their operations to deliver top-quality products quickly. In this dynamic environment, automated robots Manufacturing drive transformation, providing unmatched efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility.
Modern factory floors are filled with automation, where automated robots Manufacturing and humans work together seamlessly. From car manufacturers to electronics makers, companies in various industries use automated robots Manufacturing to streamline operations, improve quality, and promote sustainable growth.
Discover how various Robots in the Manufacturing Industry boost efficiency and innovation.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
History of Robots in Manufacturing
The journey of robots in manufacturing began in the 1960s with the introduction of the Unimate, the first industrial robot. Developed by George Devol and Joseph Engelberger, Unimate revolutionized the automotive industry by performing repetitive tasks such as welding and material handling. Since then, robotic technology has evolved rapidly, with advancements in sensors, programming, and artificial intelligence (AI) leading to the sophisticated machines we see today.
Types of Manufacturing Robots
Industrial Robots Industrial robots are versatile and reliable powerhouses at the heart of the manufacturing revolution. Equipped with advanced sensors and sophisticated programming, these robots excel in various tasks, including welding, painting, assembly, and material handling. With their tireless efficiency and precision, industrial robots have become indispensable assets in factories worldwide, driving productivity and innovation.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Collaborative robots, or cobots, have emerged as game-changers in the quest for efficiency and safety. Unlike traditional robots, cobots are designed to work alongside humans, augmenting rather than replacing human labor. Equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and intuitive programming, cobots bring flexibility and adaptability to the manufacturing floor, enabling seamless collaboration between man and machine.
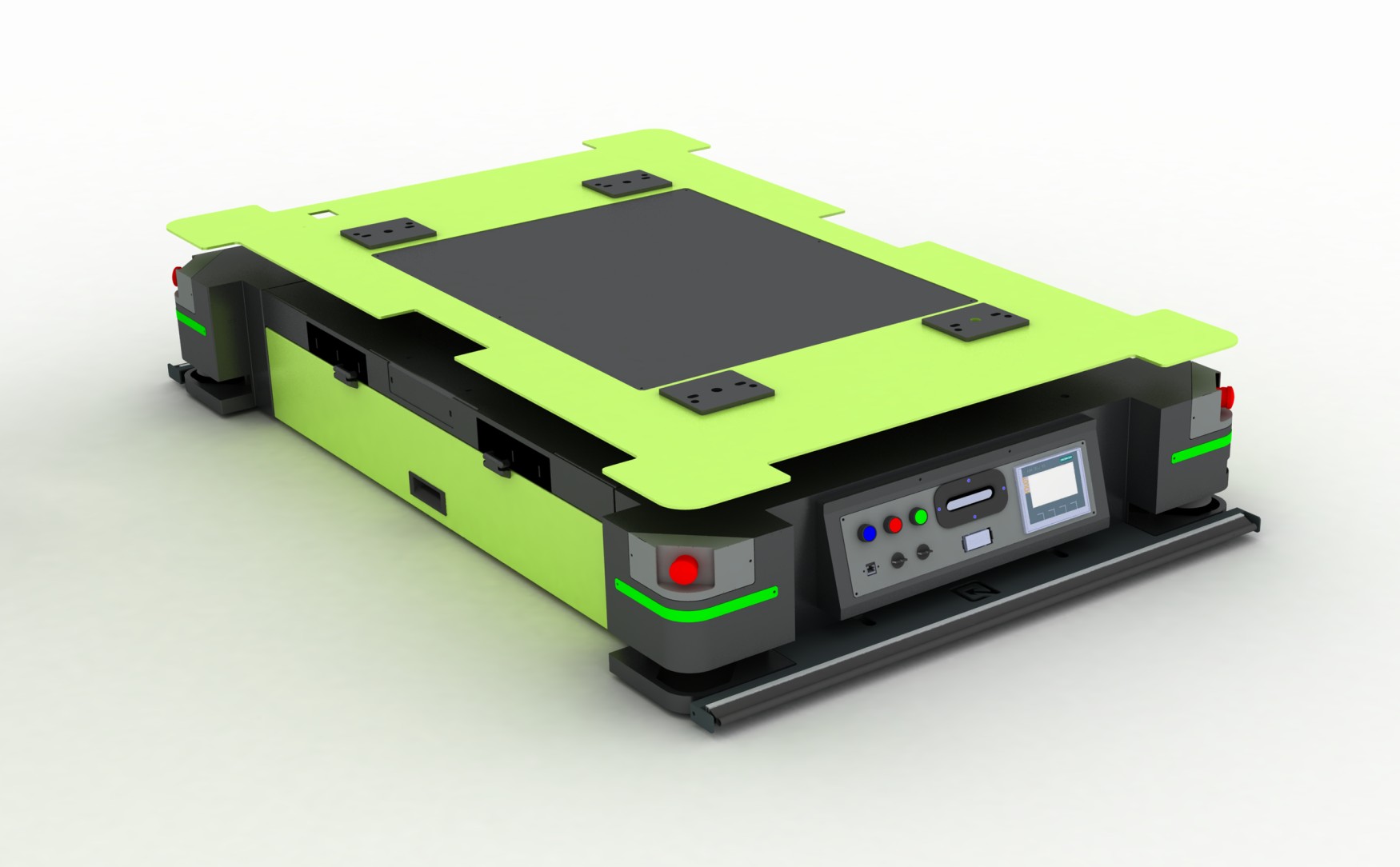
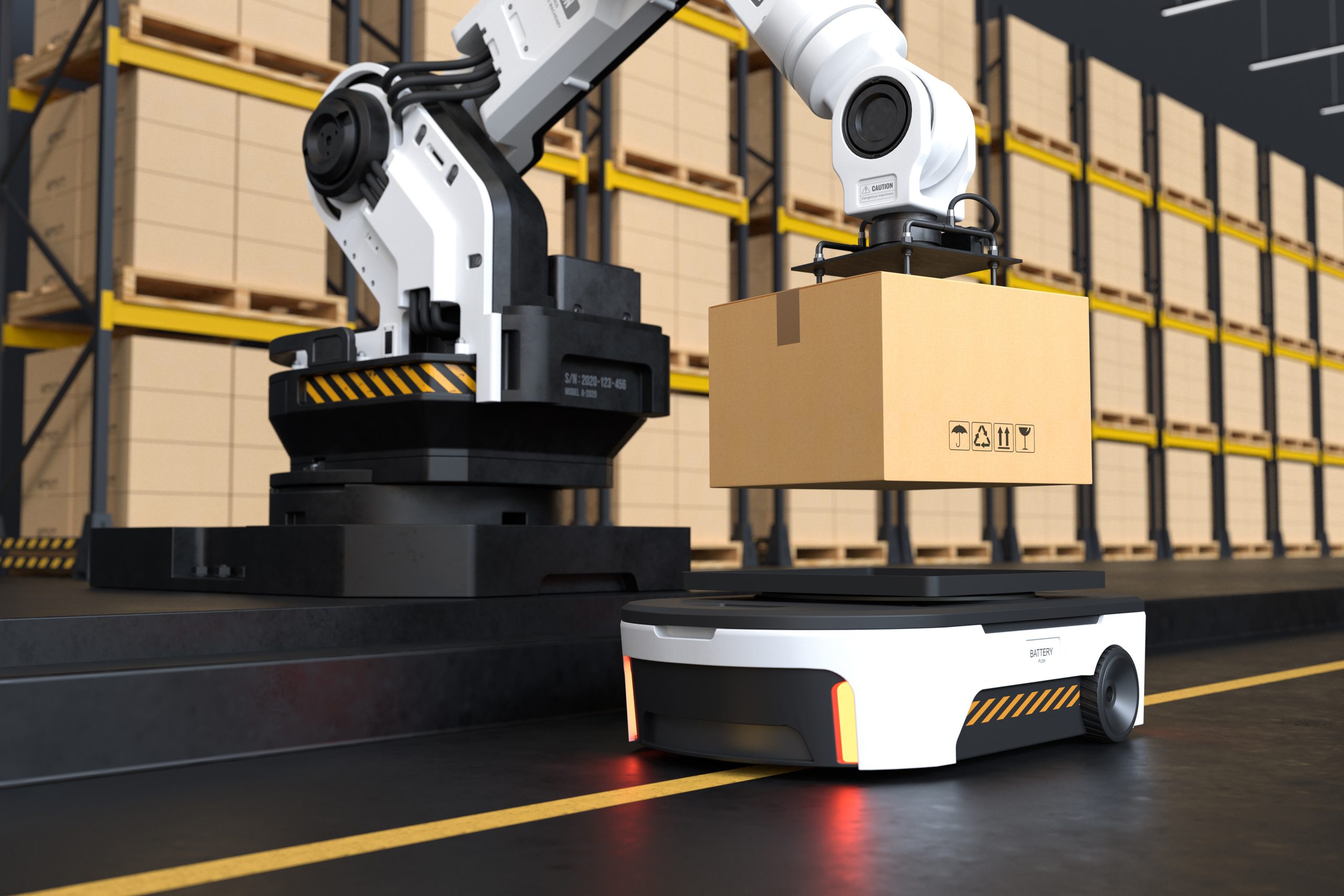
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) Autonomous mobile robots Manufacturing represent a paradigm shift in manufacturing logistics. These agile machines, equipped with advanced navigation systems and intelligent sensors, roam the factory floor with unparalleled autonomy and efficiency. From material transport and inventory management to order fulfillment and logistics, AMRs offer a versatile solution to modern manufacturing’s complex challenges, driving efficiency and agility across the supply chain.
SCARA Robots Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) robots embody precision and speed in vertical assembly applications. With their articulated arm design and advanced control systems, SCARA robots excel in tasks such as pick-and-place operations, packaging, and machine tending, driving efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing processes.
Delta Robots Characterized by their parallel-link structure, delta robots are the epitome of speed and agility in high-speed picking and packaging applications. These nimble machines are the backbone of industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, where rapid and precise motion is paramount to success.
Cylindrical Robots: Cylindrical robots operate within a cylindrical work envelope, combining a rotary base, a vertical axis, and an extending arm. They are ideal for tasks like assembly, material handling, and machine tending in confined spaces. Their design allows for efficient movement along vertical and horizontal planes.
Applications of Robotics
Assembly
Automated robots Manufacturing play a pivotal role in the assembly process, where precision and efficiency are paramount. From automotive assembly lines to electronics manufacturing, robots streamline operations by executing repetitive tasks with unmatched accuracy.
Welding and Fabrication
In the realm of metalworking, industrial robots have revolutionized welding and fabrication processes. These robots perform intricate welds with consistency and speed, ensuring uniformity and structural integrity in the final product.
Material Handling
Material handling represents a significant area of opportunity for automation. Autonomous mobile robots Manufacturing excel in transporting raw materials, components, and finished goods within manufacturing facilities, optimizing workflow, and reducing labor costs.
Painting and Finishing
Industrial robots equipped with painting and finishing capabilities have transformed the automotive and aerospace industries. These robots apply coatings with precision, consistency, and minimal overspray, resulting in high-quality finishes while reducing material waste.
Quality Control
Automated robots Manufacturing are increasingly being deployed for quality control purposes, where they inspect products for defects, deviations, and inconsistencies. Through advanced vision systems and machine learning algorithms, these robots ensure adherence to stringent quality standards, minimizing defects and rework.
Packaging and Palletizing
Delta robots are commonly utilized for packaging and palletizing applications due to their unparalleled speed and agility. These robots excel in picking, sorting, and placing items onto pallets or packaging containers, optimizing throughput and reducing manual labor.
Inspection and Testing
Automated robots Manufacturing equipped with sensors and vision systems are employed for inspection and testing tasks across various industries. From detecting surface defects to performing non-destructive testing, these robots enhance product quality and reliability while reducing inspection cycle times.
Benefits of Robotics in Manufacturing
Increased Efficiency
Automated robots Manufacturing perform tasks faster and more accurately than human workers. This leads to significant improvements in productivity and throughput, enabling factories to handle larger volumes of goods with the same or fewer resources.
Enhanced Accuracy
Robots minimize the risk of human error in tasks such as picking, packing, and quality control. This leads to higher order accuracy and reduces the incidence of returns and customer complaints.
Cost Savings
While the initial investment in automation can be high, the long-term cost savings are considerable. Automation reduces labor costs, minimizes waste, and improves resource utilization, leading to overall cost efficiency.
Scalability
Automated systems can be scaled up or down to meet changing business needs. This flexibility allows companies to respond quickly to market demands and seasonal fluctuations without significant manual intervention.
Improved Safety
Robots reduce the need for manual handling of goods, minimizing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. This leads to a safer working environment and can also reduce insurance costs.
Better Space Utilization
Automated systems can optimize the use of factory space. Vertical lift modules and AS/RS systems, for example, make use of vertical space, allowing warehouses to store more goods in the same footprint.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
With automation, factories can process orders more quickly and accurately, leading to faster shipping times and fewer errors. This improved service level can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When to Automate Your Warehouse
Determining the right time to automate involves evaluating factors such as production volume, labor costs, and operational inefficiencies. Companies experiencing high error rates, increased labor costs, and significant production delays should consider automation to streamline their processes and improve productivity.
Challenges of Warehouse Automation
High Initial Investment
The cost of procuring and installing automated systems can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This includes the expense of hardware, software, and the infrastructure required to support these technologies.
Integration Complexity
Integrating automated systems with existing warehouse operations and legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming. Ensuring seamless communication between different technologies and maintaining data consistency is crucial for the success of automation projects.
Skilled Workforce Requirement
Operating and maintaining automated systems require specialized skills. Companies need to invest in training their workforce or hiring skilled technicians, which can be a significant challenge in regions with a limited talent pool.
Technological Obsolescence
Rapid advancements in technology mean that automated systems can become outdated quickly. Companies need to stay abreast of the latest developments and be prepared for frequent upgrades to maintain operational efficiency.
Downtime and Maintenance
Automated systems, like any machinery, require regular maintenance and are prone to occasional breakdowns. Unplanned downtime can disrupt warehouse operations and lead to delays in order fulfillment.
Transforming Manufacturing Robotics with Cutting-Edge Technologies
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing manufacturing robotics, making them smarter, more autonomous, and deeply integrated into the Industry 4.0 framework.
1. Smarter and Autonomous Robots
AI and ML enable robots to learn and adapt to dynamic environments, improving precision, decision-making, and task efficiency. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) with sensors and AI navigate factory floors, optimizing workflows and reducing downtime.
2. Collaborative Cobots
Collaborative robots (cobots), enhanced with AI and IoT, work safely alongside humans, automating repetitive tasks while learning from human interactions. They are increasingly used in assembly lines, quality control, and material handling, bridging the gap between human intelligence and machine efficiency.
3. Integration with Industry 4.0
IoT connects robots to a network of smart devices, enabling real-time data sharing and predictive maintenance. Robots integrated with cloud platforms can analyze vast datasets, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure seamless communication across manufacturing ecosystems.
Key Trends
- Predictive Analytics: AI-powered robots can foresee maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime.
- Customizable Manufacturing: ML enables robots to adjust to unique product designs, supporting agile manufacturing.
- Sustainability: Smart robots optimize energy consumption and minimize waste, aligning with eco-friendly initiatives.
The fusion of AI, IoT, and ML is not just enhancing robotic capabilities but also redefining the future of manufacturing, enabling faster production, higher flexibility, and smarter, interconnected systems.
Conclusion
Automated robots Manufacturing have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, driving unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. From traditional industrial robots to cutting-edge autonomous mobile robots, these machines continue to redefine the boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing. As we look to the future, the integration of automation will only intensify, paving the way for greater advancements in robotics technology.
Are you ready to unlock the full potential of automation in manufacturing? Contact us at Novus Hi-Tech to explore how our comprehensive range of automated solutions, including autonomous mobile robots Manufacturing, can transform your operations and propel your business into the future.