In the era of Industry 4.0, the concept of smart factories and smart manufacturing has gained significant attention. These digitized manufacturing facilities are revolutionizing the way products are made by utilizing advanced technologies and data analysis.
In this blog, we will explore what exactly a smart factory is and how it differs from smart manufacturing. We will also delve into the key components of smart factories and the advantages they offer in the future of manufacturing.
What Is A Smart Factory?
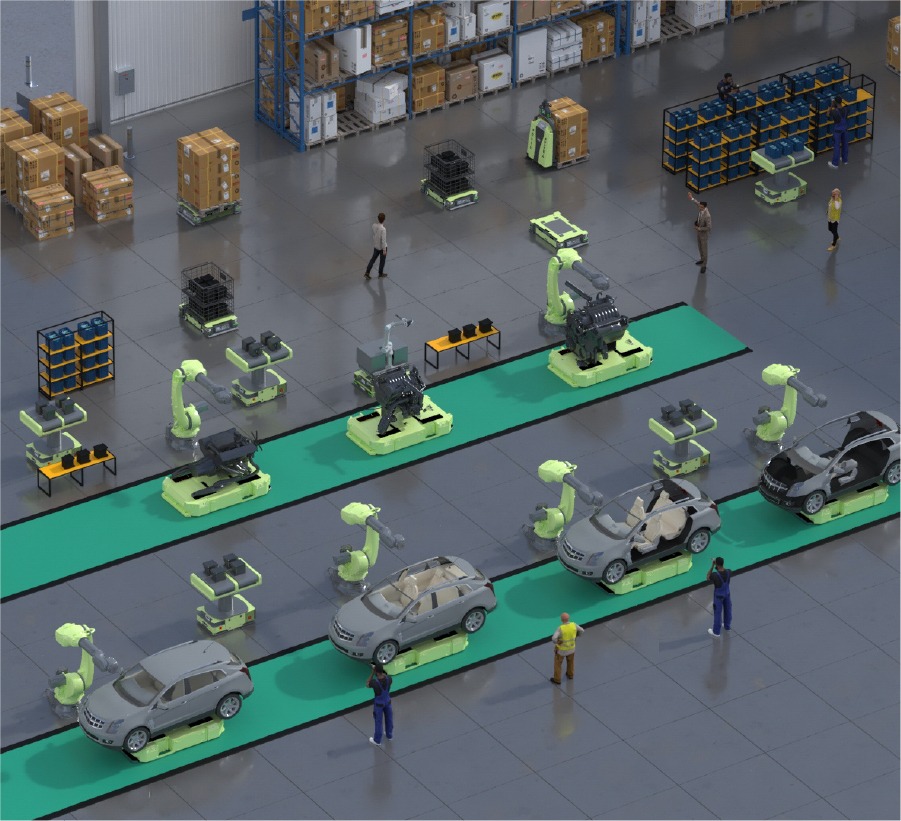
A smart factory is a digitized manufacturing facility that uses connected devices, machinery, and production systems to continuously collect and share data. This data is then used to inform decisions to improve processes as well as address any issues that may arise.
The smart manufacturing practices used by a smart factory are enabled by a variety of technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, cloud computing, and the industrial Internet of Things (IoT). Smart factories connect the digital and physical worlds to monitor an entire production process, from supply chain management to manufacturing tools and even the work of individual operators on the shop floor. Fully integrated, collaborative manufacturing systems provide a range of benefits for operators, including allowing operations to be adaptable and readily optimized.
Benefits of Smart Factories:
- Operational Efficiency
- Reduce Downtime
- Streamline Operations
- Predictive Maintenance
- Real-Time Visibility
- Higher Productivity
- Reduce Costs
- Enhance Competitiveness
Why Is Embracing Smart Facts Now Imperative?
As technology continues to advance, manufacturers need to embrace smart factory practices to stay competitive in the market. By adopting smart factories, manufacturers can leverage the power of digital transformation to optimize their production processes and adapt to changing consumer demand.
By adopting smart manufacturing practices as soon as possible, businesses can position themselves as leaders in their industry and harness the benefits of increased efficiency, agility, and sustainability.
What Is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is the application of advanced technologies and data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes and improve efficiency. It involves the integration of technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, cloud computing, and the industrial Internet of Things (IoT) to enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making.
Smart manufacturing aims to transform traditional manufacturing practices by digitizing and connecting the entire production process, from supply chain management to production tools and systems.
Benefits Of Smart Manufacturing.
- Lower Costs
- Optimizes Production Processes
- Reducing Waste
- Minimizing Downtime
- Greater Flexibility
- Insights Into The Production Process
- Improve Efficiency
- Real-Time Visibility
- Operational Excellence
Why Embrace Smart Manufacturing?
Integrating smart manufacturing into your company can provide numerous benefits and give you a competitive edge in the market. By embracing advanced technologies and data analytics, you can optimize your production processes, improve efficiency, and deliver high-quality products promptly. Real-time monitoring and analytics enable you to make data-driven decisions, identify bottlenecks, and proactively address issues. Smart manufacturing also allows for better supply chain management, with real-time visibility into inventory levels, demand, and logistics. This enables you to streamline operations, reduce lead times, and meet customer expectations more effectively.
Additionally, smart manufacturing facilitates better collaboration and communication across different departments and stakeholders, leading to improved coordination and streamlined workflows.
By implementing smart manufacturing practices, you can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and position your company for long-term success in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Smart Factory vs. Smart Manufacturing: Understanding the Difference
While the terms smart factory and smart manufacturing are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. A smart factory refers to a digitized manufacturing facility that utilizes advanced technologies and data analytics to optimize production processes and improve efficiency.
On the other hand, smart manufacturing is a broader concept that encompasses the application of these technologies and practices throughout the entire manufacturing ecosystem, including supply chain management, production tools, and systems.
While a smart factory is a component of smart manufacturing, the latter encompasses a more comprehensive approach to digitizing and optimizing the entire manufacturing process.
Discover how Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing boost efficiency and innovation.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
Key Components of Smart Factories
Smart factories rely on various technologies and components to enable their digitized and connected operations. These components include:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT integration connects devices and machinery on the shop floor, enabling real-time data collection and sharing. This allows companies to monitor production processes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize workflows. For instance, temperature sensors ensure climate control for optimal production conditions.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML enable advanced data analysis and decision-making. AI identifies patterns and anomalies, while ML uses this data for predictive insights and process optimization. For example, these technologies can predict product defects and address them proactively through predictive quality assurance.
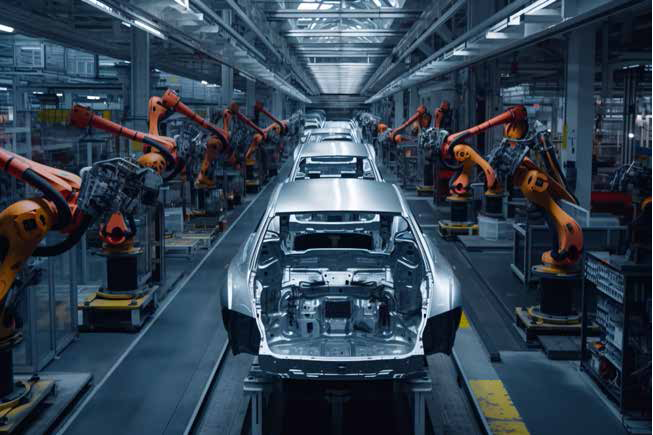
3. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation enhance efficiency by performing repetitive and complex tasks with precision. They streamline production processes, reduce errors, and adapt quickly to market demands, minimizing downtime and optimizing resource utilization.
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing supports scalable data storage, processing, and real-time analysis. It facilitates collaboration, enables remote monitoring, and ensures seamless communication across the manufacturing ecosystem. Cloud systems enhance data-driven decision-making while improving coordination.
5. Cybersecurity Measures
Smart factories implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect data integrity and system security. These include secure network architecture, data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to mitigate risks and safeguard against cyber threats.
6. Big Data Analytics
Big data enables predictive and advanced analytics, allowing businesses to derive meaningful insights and drive innovation. Smart factories leverage large data sets to optimize processes and create actionable strategies for improvement.
7. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IIoT networks connect devices and machines with digital communication capabilities. These networks enable automated workflows and provide real-time data on equipment status and activities, ensuring efficient operations.
8. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a machine or system, enabling testing, innovation, and risk-free optimization. This minimizes resource wastage and enhances creativity in process development.
9. Additive Printing (3D Printing)
3D printing supports on-demand manufacturing, reducing waste and inventory risks. It is particularly valuable during supply chain disruptions or sudden product demand, ensuring just-in-time production.
10. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR provide immersive, real-time data visualization for factory operations. These technologies enhance awareness of factory status, streamline training, and improve operational decision-making.
11. Blockchain
Blockchain enhances security in smart factories by managing access to connected assets and systems. It ensures the accuracy of records, facilitates smart contracts, and tracks goods throughout the supply chain journey.
12. Modern Databases
In-memory databases and advanced ERP systems drive smart factory operations by managing complex data analytics and processes. These modern systems overcome the limitations of traditional, disk-based databases, ensuring optimal functionality.
Enhance Productivity: Transform Smart Manufacturing with Novus Hi-Tech
Novus Hi-Tech is a leading-edge technology provider that specializes in transforming manufacturing processes through smart factories and smart manufacturing. By leveraging advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and machine learning, Novus Hi-tech enables companies to optimize their production processes, enhance productivity, and embrace the future of manufacturing.
With a focus on consumer demand and virtual reality, Novus Hi-Tech empowers manufacturers to achieve operational excellence, improve quality control, and drive innovation. With a track record of successful implementations and a customer-centric approach, Novus Hi-Tech is the ideal partner for companies looking to transform their manufacturing operations and embrace the future of manufacturing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embracing the concepts of smart factories and smart manufacturing is crucial for many reasons. By integrating advanced technologies, industries can pave the way for a sustainable and quality-driven future.
As we look towards the future, adopting smart factories and smart manufacturing practices becomes imperative for businesses aiming to stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape. To explore the potential of this innovative paradigm, get in touch with us today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key benefits of implementing smart manufacturing in a factory?
Implementing smart manufacturing offers several key benefits, including operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, improved product quality, optimized supply chain management, and cost savings through lower costs and increased productivity.
How does smart manufacturing improve efficiency and productivity in industrial settings?
Smart manufacturing improves efficiency and productivity through real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automation.
What role does artificial intelligence play in smart manufacturing processes?
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in smart manufacturing processes by enabling advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and automation. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns and anomalies, and make data-driven decisions, leading to improved efficiency and quality control.
How can IoT (Internet of Things) devices be utilized in a smart factory environment?
IoT devices in a smart factory environment can collect and share data from connected devices and machinery, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of production processes.
What are the challenges associated with transitioning to a smart manufacturing model?
Transitioning to a smart manufacturing model can present challenges such as the need for extensive data collection and analysis capabilities, the integration of diverse technologies, cybersecurity risks, and the need for retraining and upskilling the workforce.
What is the role of robotics and automation in the context of smart manufacturing?
Robotics and automation play a crucial role in smart manufacturing by improving efficiency, reducing reliance on manual labor, and enhancing productivity. Robots and automation systems can perform repetitive and complex tasks with precision and speed, leading to increased operational efficiency and optimized production processes.
Can traditional manufacturing facilities be upgraded to smart factories, or is it more practical to build new facilities?
Upgrading traditional manufacturing facilities to smart factories is feasible but challenging due to the extensive technological overhaul required. Building new facilities tailored for smart manufacturing might offer more efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
How does connectivity between different components and systems within a smart factory enhance overall performance?
Connectivity between different components and systems within a smart factory allows for seamless coordination and integration of processes, leading to enhanced overall performance, improved efficiency, and optimized production.
What are some common misconceptions about smart manufacturing, and how can they be addressed?
Some common misconceptions about smart manufacturing include the belief that it is expensive and complex to implement.
How do smart manufacturing practices contribute to sustainability and environmental responsibility?
Smart manufacturing practices contribute to sustainability and environmental responsibility by optimizing energy usage, reducing waste, and implementing eco-friendly practices.