In the age of Industry 4.0, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have emerged as a transformative technology, reshaping how materials are handled within factories and warehouses. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of AGVs, their applications, features, benefits, and how they can revolutionize material handling in your facility.
What are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are robotic systems designed to transport materials autonomously within a manufacturing or distribution environment. These vehicles operate without human intervention, navigating predefined pathways using sophisticated guidance systems such as lasers, cameras, magnets, or a combination of these technologies. AGVs are a cornerstone of modern material handling solutions, significantly enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety in industrial operations.
Discover how Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) transform efficiency and productivity.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
History and Evolution of AGVs
The development of AGVs began in the 1950s with the introduction of automated tow vehicles that followed a fixed path guided by wires embedded in the floor. Over the decades, AGVs have evolved dramatically, incorporating advanced technologies like laser navigation, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. Today, AGVs are capable of performing complex tasks with high precision, adaptability, and reliability, making them integral to smart factory ecosystems.
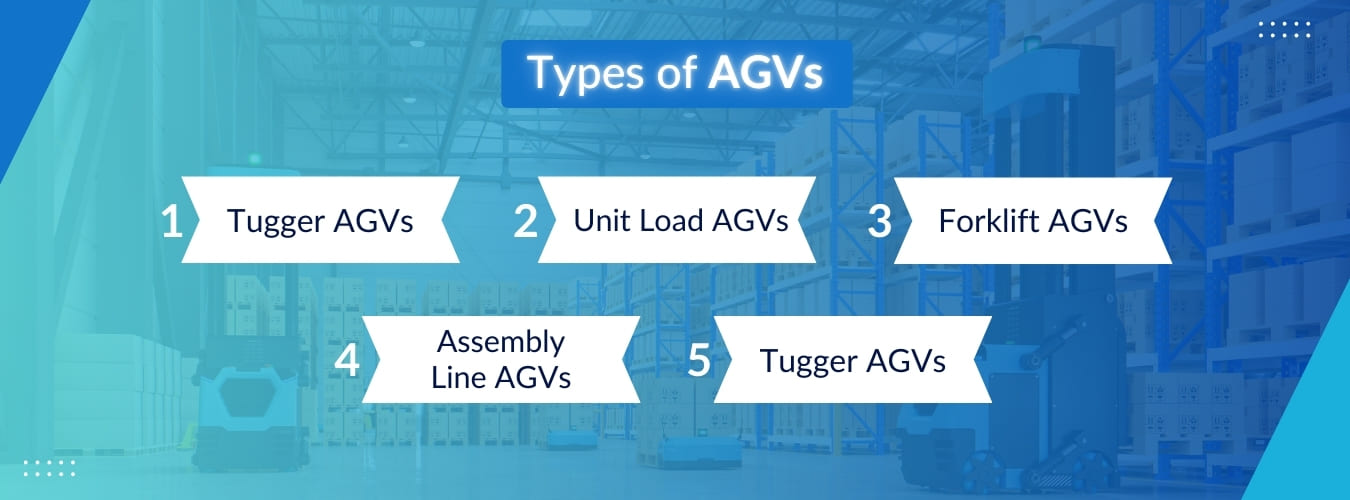
Types of AGVs
Understanding the different types of AGVs is essential for choosing the right solution for your specific needs. Here, we explore the primary categories of AGVs and their typical applications:
1. Tugger AGVs
Tugger AGVs are designed to pull carts, trailers, or trains of loads. They are ideal for transporting large volumes of materials over long distances within a facility. Commonly used in the automotive industry, tugger AGVs efficiently move parts and components between different production areas, ensuring a smooth and continuous flow of materials.
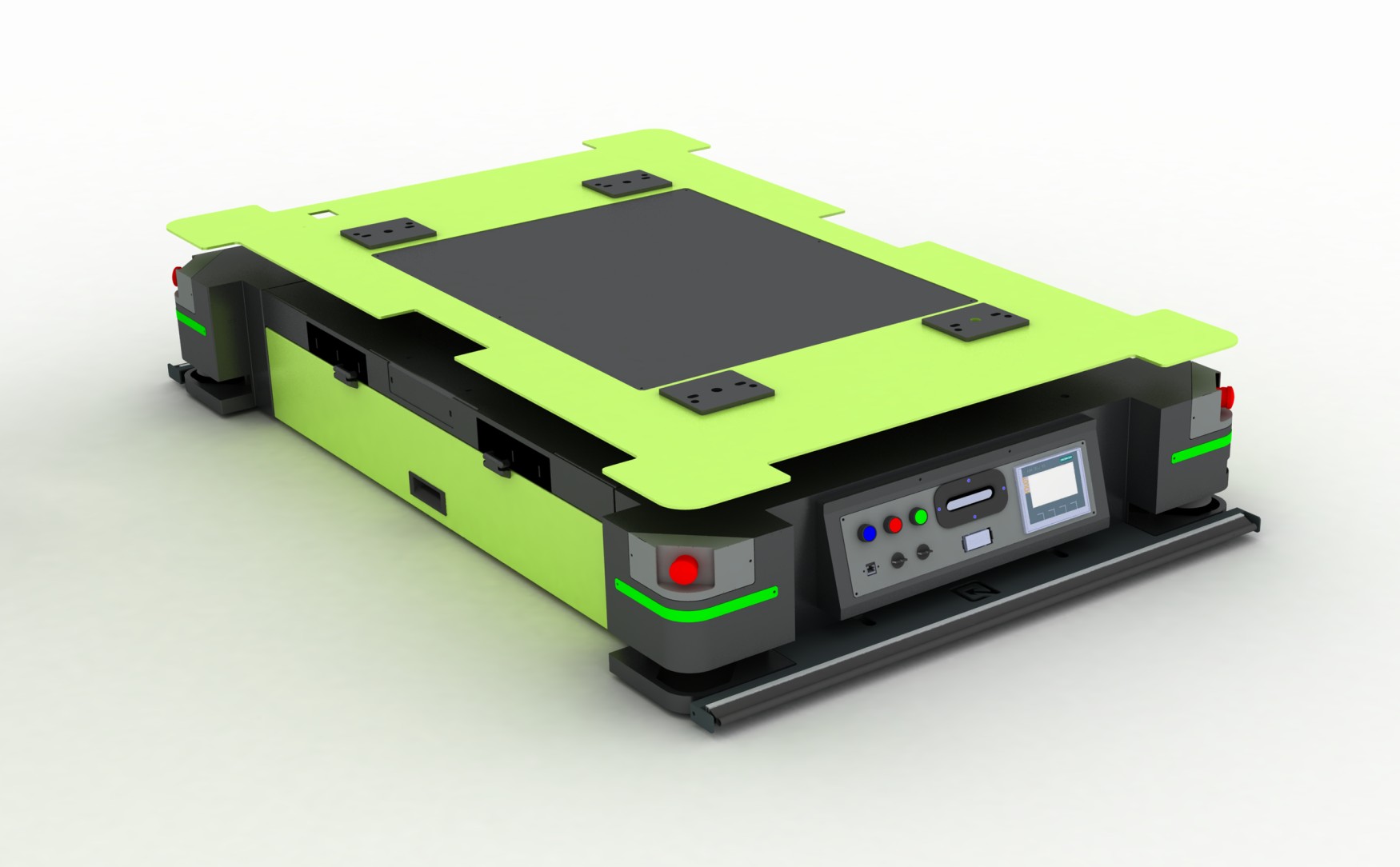
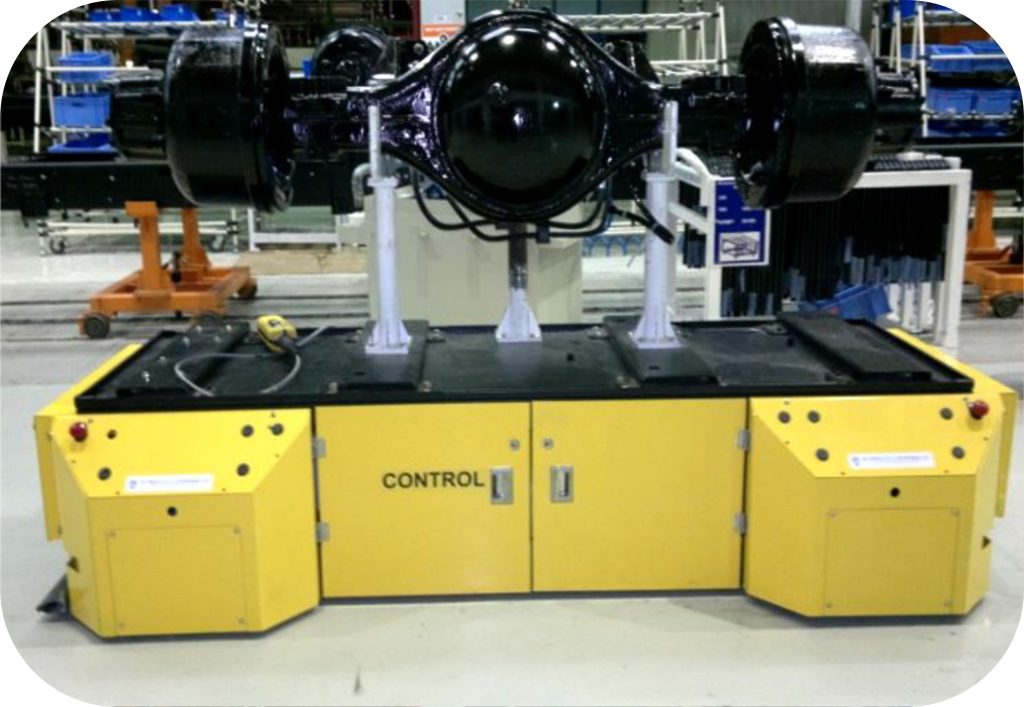
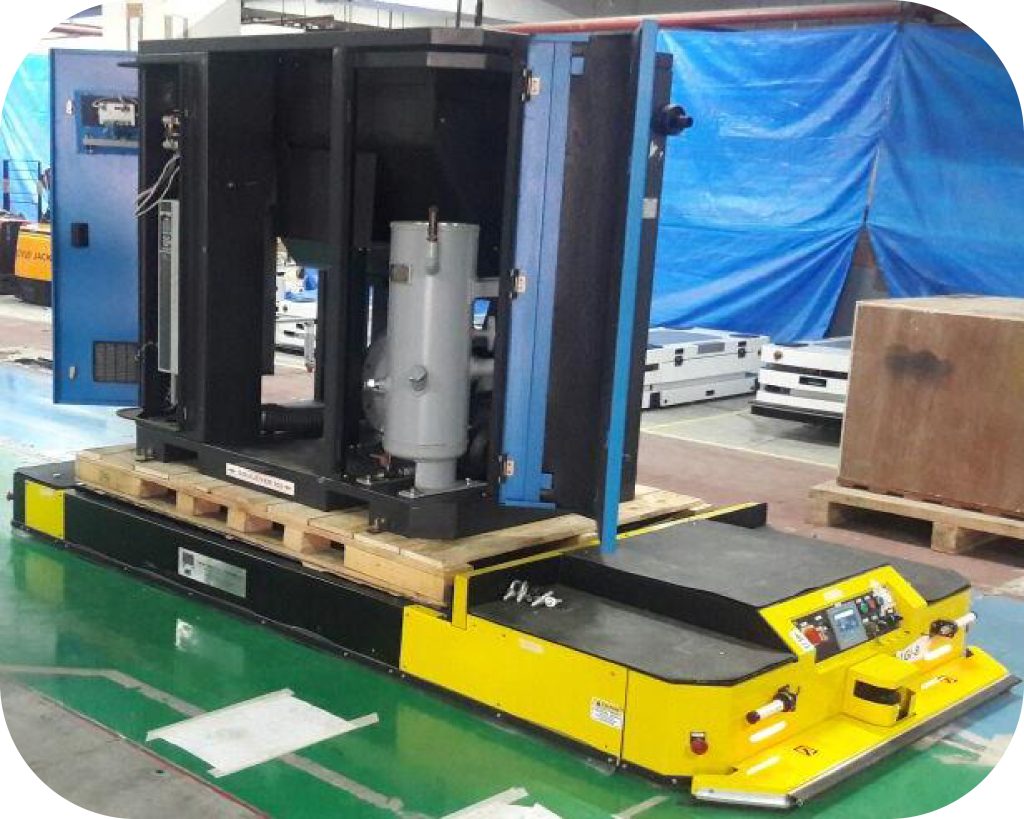
2. Unit Load AGVs
Unit Load AGVs are equipped with platforms or conveyor decks to transport single items, pallets, or containers. These AGVs are particularly useful in applications that require the movement of discrete loads, such as in warehousing and distribution centers. They enhance the efficiency of inventory management by automating the transfer of goods between storage locations and production areas.
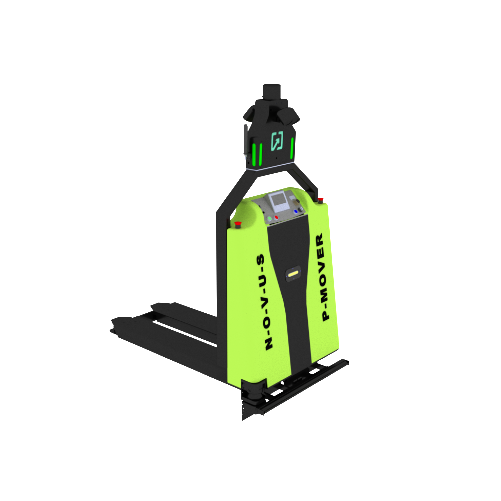
3. Forklift AGVs
Forklift AGVs replicate the functions of traditional forklifts but operate autonomously. They can lift, transport, and stack pallets, making them suitable for environments where repetitive pallet movement is necessary. These AGVs are commonly found in warehouses and distribution centers, where they contribute to streamlined logistics and reduced labor costs.
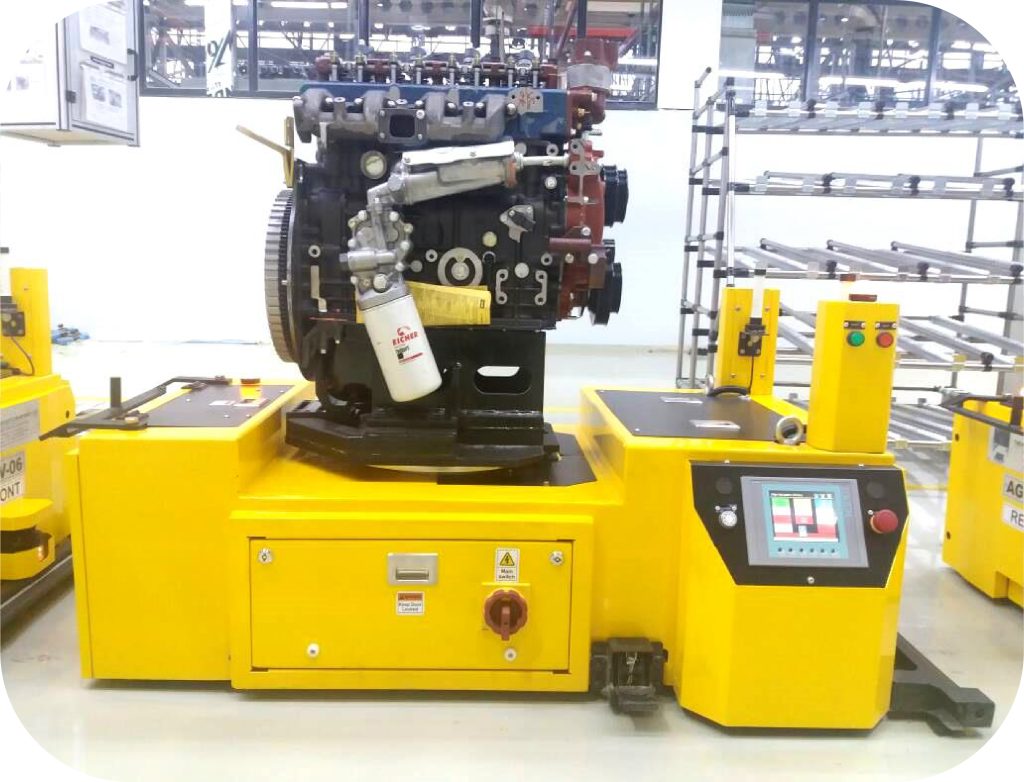
4. Assembly Line AGVs
Assembly Line AGVs are specialized for supporting production processes by delivering parts and materials to specific locations on the assembly line. These AGVs ensure a steady supply of components, minimizing production downtime and enhancing productivity. They are widely used in industries such as automotive and electronics manufacturing.
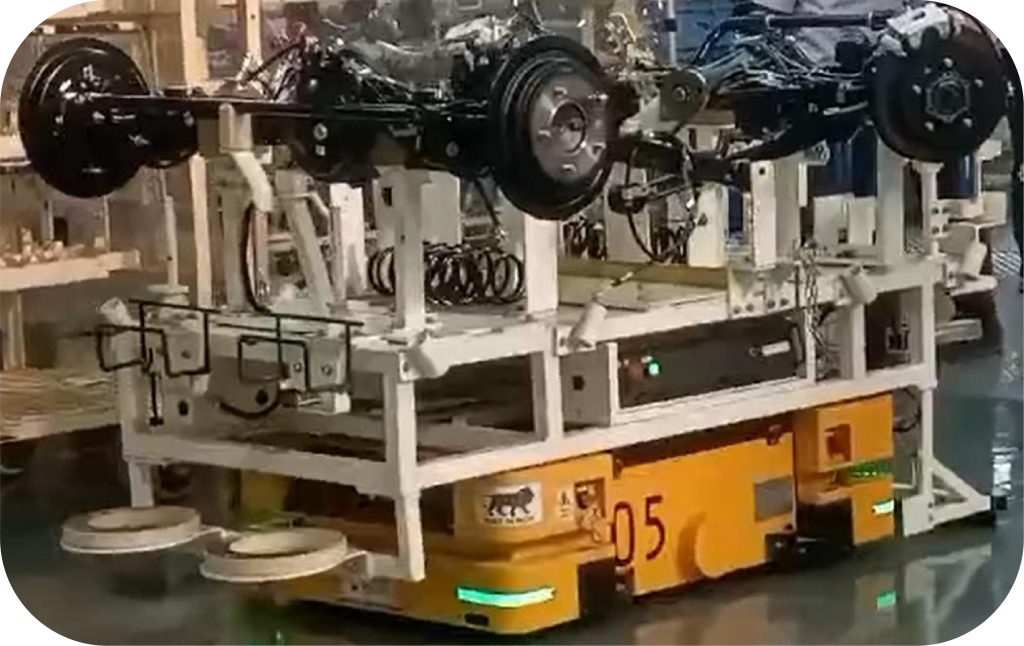
5. Mobile Robots
Mobile Robots represent the most advanced form of AGVs, equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and AI-driven software that allow them to navigate complex environments and perform a variety of tasks. These robots are highly adaptable and can be employed for diverse applications, ranging from material handling to inspection and maintenance.
Key Features of AGVs
AGVs are packed with features that make them indispensable in modern industrial operations. Here are some of the key features that set AGVs apart:
Advanced Navigation Systems
AGVs use advanced navigation technologies such as laser guidance, vision systems, magnetic tracks, and inertial navigation to follow precise paths. These systems enable AGVs to navigate complex environments with high accuracy, avoiding obstacles and ensuring efficient material transport.
Safety Mechanisms
Safety is paramount in any industrial setting. AGVs are equipped with a multitude of safety features, including sensors, cameras, and emergency stop functions. These mechanisms detect obstacles and human presence, preventing collisions and ensuring safe operation around workers.
Flexibility and Scalability
AGVs are designed to be flexible and adaptable to different operational layouts. They can be easily reprogrammed or reconfigured to handle various tasks, making them suitable for evolving business needs. This scalability allows facilities to expand their operations without significant additional investment, accommodating growth and changes in production demands.
Energy Efficiency
Modern AGVs are powered by efficient battery systems that minimize energy consumption. Many AGVs feature automated charging capabilities, ensuring they remain operational around the clock without significant downtime. This energy efficiency not only reduces operational costs but also supports sustainability initiatives.
Real-time Data Monitoring
AGVs are integrated with warehouse management systems (WMS) and manufacturing execution systems (MES), enabling real-time data monitoring and analytics. This integration provides valuable insights into operational performance, allowing for better decision-making and process optimization. Real-time data helps in tracking inventory, predicting maintenance needs, and improving overall efficiency.
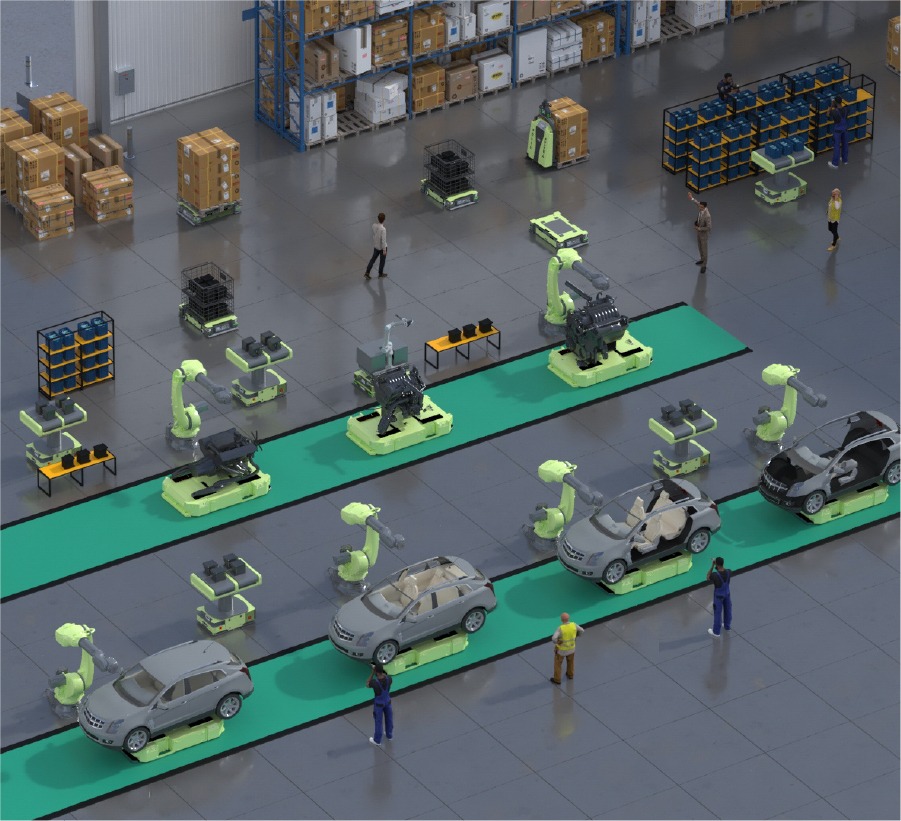
Applications of AGVs in Factories
AGVs are versatile machines that can be employed in various industrial settings to streamline operations. Here are some key applications of AGVs in factories:
Material Transport
One of the primary applications of AGVs is the transport of materials within a facility. AGVs can move raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished products between different areas, ensuring a seamless flow of materials through the production process. This automation reduces manual handling, speeds up material movement, and enhances overall efficiency.
Inventory Management
AGVs play a crucial role in inventory management by automating the movement and storage of goods. They can transport items to and from storage locations, assisting in accurate inventory tracking and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Automated inventory management with AGVs leads to better space utilization, reduced handling errors, and improved inventory accuracy.
Assembly Line Support
In assembly line operations, AGVs deliver parts and components to specific locations, ensuring a steady supply and minimizing production downtime. This application is particularly valuable in industries such as automotive and electronics manufacturing, where just-in-time (JIT) delivery is critical to maintaining continuous production flow.
Packaging and Shipping
AGVs can automate the movement of packaged goods to shipping areas, streamlining the order fulfillment process. By reducing manual handling, AGVs improve the speed and accuracy of packaging and shipping operations. This automation enhances throughput, reduces errors, and ensures timely delivery of products.
Waste Removal
AGVs can be used to transport waste materials and recyclables to designated disposal areas. This application helps maintain a clean and efficient workspace, reducing the risk of contamination and improving overall productivity. Automated waste removal also supports environmental sustainability by ensuring proper segregation and disposal of waste materials.
Benefits of Implementing AGVs
The adoption of AGVs in factories offers numerous benefits, making them a valuable investment for any manufacturing operation. Here are some of the key benefits of implementing AGVs:
Increased Efficiency
AGVs operate 24/7, significantly increasing the efficiency of material handling processes. By automating repetitive tasks, AGVs free up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities. This continuous operation ensures a steady flow of materials and minimizes bottlenecks in the production process.
Cost Savings
AGVs reduce labor costs by minimizing the need for manual handling of materials. They also decrease the likelihood of errors and damage associated with manual processes, resulting in cost savings. Additionally, AGVs’ energy efficiency and low maintenance requirements contribute to overall operational cost reduction.
Improved Safety
AGVs lower the risk of workplace accidents and injuries by automating hazardous tasks. Their advanced safety features ensure safe operation around human workers, creating a safer working environment. By reducing the need for manual material handling, AGVs help prevent injuries such as strains, sprains, and repetitive stress injuries.
Enhanced Productivity
AGVs ensure a constant flow of materials, minimizing production downtime and enhancing overall productivity. Their ability to operate continuously and efficiently contributes to smoother and more reliable operations. This increased productivity enables manufacturers to meet production targets, improve delivery times, and respond quickly to changes in demand.
Scalability
AGVs are easily scalable to meet the evolving needs of the business. As operations grow, additional AGVs can be integrated into the system without significant disruption. This scalability allows for flexible and future-proof operations, enabling manufacturers to adapt to changing market conditions and production requirements.
The Future of AGVs
The future of AGVs is bright, with advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies set to further enhance their capabilities. Here are some trends and innovations to watch for:
Increased Autonomy
Future AGVs will be equipped with more advanced AI and machine learning algorithms, enabling them to make complex decisions and adapt to dynamic environments. This increased autonomy will allow AGVs to perform more sophisticated tasks with minimal human intervention, such as dynamic path planning, obstacle avoidance, and real-time decision-making.
Improved Navigation and Localization
Advancements in sensor technologies and real-time data processing will enhance the navigation and localization capabilities of AGVs. This will enable them to navigate more accurately and efficiently, even in highly dynamic and complex environments. Enhanced navigation systems will support more flexible and adaptive operations, allowing AGVs to respond to changes in the environment and optimize their routes.
Integration with IIoT
The integration of AGVs with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) will enable seamless communication between AGVs and other automated systems. This connectivity will create a fully connected and smart factory, optimizing operations and improving overall efficiency. IIoT integration will facilitate data sharing, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring, leading to more informed decision-making and proactive management of the production process.
Enhanced Human-Machine Collaboration
Future AGVs will be designed to collaborate more effectively with human workers. With improved safety features and intuitive interfaces, AGVs will work alongside humans, augmenting their capabilities and enhancing productivity. This human-machine collaboration will create more flexible and adaptive production environments, where AGVs can support and complement human tasks.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are transforming material handling in factories, delivering unmatched efficiency, safety, and flexibility. By automating tasks like material transport, inventory management, assembly line support, and waste removal, AGVs streamline operations, reduce costs, and boost productivity. Their continuous operation ensures a steady flow of materials, minimizing production downtime, while advanced navigation and safety features enhance workplace safety. Seamlessly integrating with existing systems, AGVs are a scalable, future-proof investment for businesses looking to stay competitive.
Novus Hi-Tech, a leading AGV manufacturer, has successfully implemented AGV automation for renowned companies like VECV, John Deere, Maruti Suzuki, Honda 2 Wheeler, and Asian Paints. Our expertise in delivering tailored, reliable solutions underscores our commitment to helping businesses optimize their operations. As advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technologies propel AGV capabilities forward, the integration with Industrial IoT will enable fully connected smart factories, driving unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity.
FAQs
What are the components of AGV?
AGVs are composed of the following key components:
- Chassis/Frame: The structural body that houses all other components.
- Battery: Provides power for mobility and operation of on-board systems.
- Motor: Drives the AGV and its wheels. Common types include DC or AC motors.
- Navigation System: Determines the path and guides the AGV, using technologies like laser, magnetic tape, vision, or GPS.
- Sensors: Includes proximity sensors, safety lasers, and cameras for obstacle detection and collision avoidance.
- Controller/On-board Computer: Manages communication, navigation, and operations of the AGV.
- Communication System: Facilitates interaction with the central control system or other AGVs.
- Payload Handling System: Includes conveyors, lifts, or robotic arms for handling goods.
Where are AGVs used?
AGVs are widely used across various industries for material handling, transportation, and automation purposes. Common applications include:
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers: For picking, packing, and transporting goods.
- Manufacturing Facilities: To move raw materials, components, or finished products between workstations.
- Automotive Industry: For assembly line support and just-in-time delivery.
- Healthcare: In hospitals to transport medical supplies, lab samples, or waste.
- Food and Beverage: For handling pallets, crates, or containers.
- Retail and E-commerce: To optimize order fulfillment and inventory movement.
- Ports and Airports: For container and baggage transportation.
Which motor is used in AGV?
AGVs commonly use DC motors or AC motors, depending on the design and application.
- DC Motors: Often used in compact and low-speed applications due to their precise control and ease of integration.
- AC Motors: Preferred for high-speed or heavy-duty AGVs because of their efficiency and durability.
Some modern AGVs also use brushless DC motors or servo motors for enhanced control, performance, and energy efficiency.
What is AGV navigation?
AGV navigation refers to the method used to guide and control the path of an Automated Guided Vehicle. Navigation systems ensure the AGV follows a predetermined route and adapts to dynamic environments. Types of navigation include:
- Magnetic Tape/Inductive Navigation: AGVs follow magnetic strips or wires embedded in the floor.
- Laser Navigation: Uses lasers and reflective targets for precise positioning.
- Vision-Based Navigation: Relies on cameras and image processing for route detection.
- GPS Navigation: Uses satellite-based positioning for outdoor or large-scale environments.
- Natural Navigation: Utilizes existing features of the environment (e.g., walls, racks) without additional infrastructure.
These systems ensure efficiency, accuracy, and safety in AGV operations.