Warehouse automation has revolutionized the logistics and supply chain industries, transforming how goods are stored, retrieved, and processed. As global trade intensifies and consumer demands evolve, the efficiency and accuracy offered by automated systems become paramount. This blog delves into warehouse automation, how it works, the types of automation, the challenges faced in implementing these systems, and the myriad benefits they offer.
Additionally, we will explore the warehouse automation market in India and its significant growth factors.
What Is Warehouse Automation?
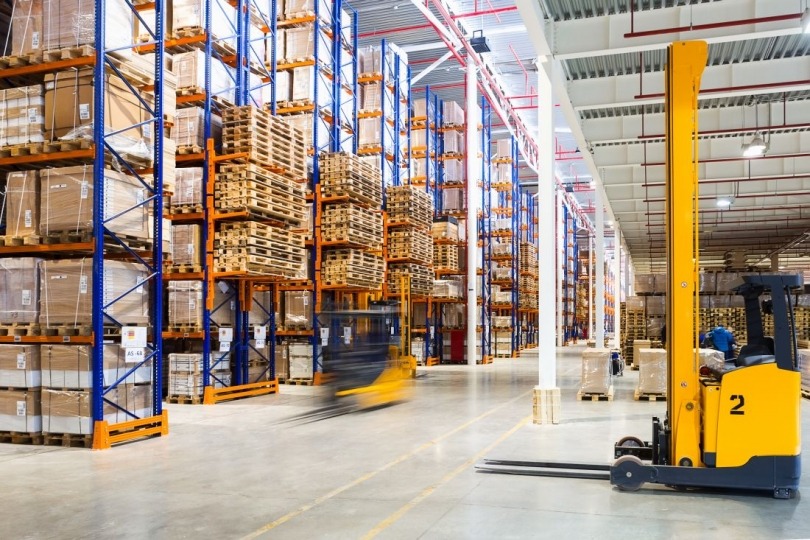
Warehouse automation refers to the use of technology to streamline and optimize warehouse operations. This includes the deployment of various automated systems and machinery to enhance the efficiency of inventory management, order processing, and data collection. By reducing the reliance on manual labor and minimizing human error, warehouse automation significantly improves operational accuracy and productivity.
Discover the types, challenges, and benefits of Warehouse Automation.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
How Warehouse Automation Works
Warehouse automation works by integrating various technologies and systems to automate tasks traditionally performed by human workers. This includes software solutions for process automation and physical automation involving machinery and robotics. Together, these systems ensure seamless operation, from inventory tracking to order fulfillment, without the need for constant human intervention.
Types of Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation can be broadly categorized into two types: process automation and physical automation.
Process Automation
Process automation involves the use of software and systems to streamline and optimize warehouse operations. Key technologies under process automation include:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): A WMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and warehouse processes, helping optimize storage, retrieval, and labor resources.
- Automated Data Collection (ADC): ADC technologies, such as barcode scanners and RFID, facilitate accurate and efficient data capture, reducing human error in inventory tracking and order processing.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): An ERP system integrates various business processes, including warehouse management, finance, and supply chain operations, providing a unified platform for data analysis and decision-making.
Physical Automation
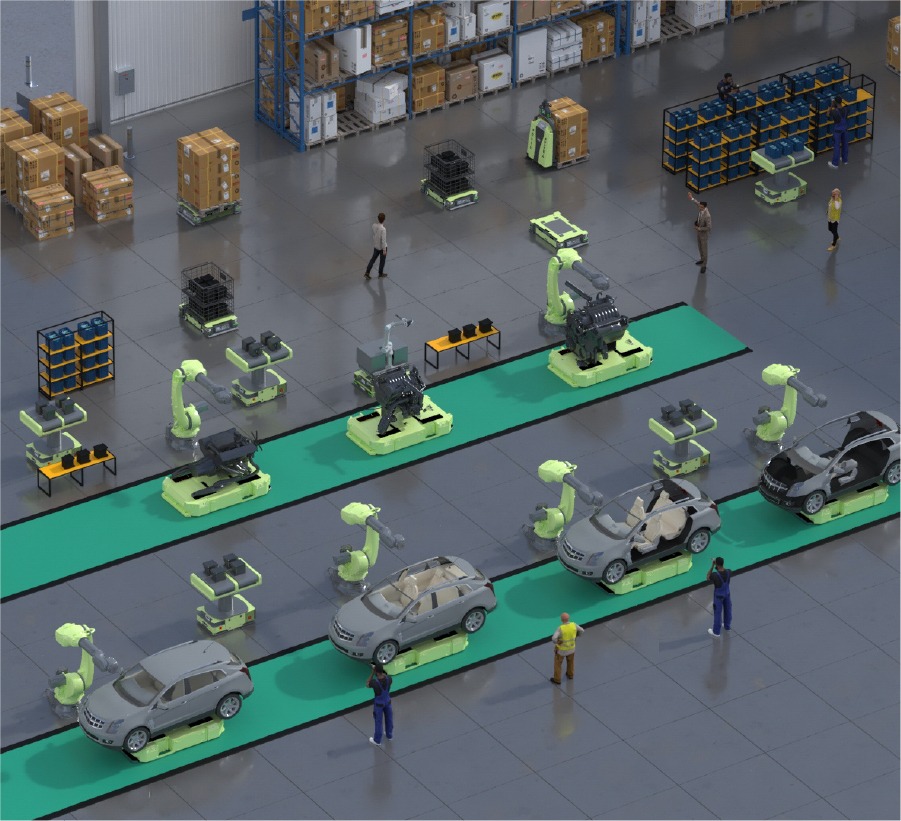
Physical automation involves using machinery and robotics to perform manual tasks within the warehouse. Key technologies under physical automation include:
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): These computer-controlled systems automatically place and retrieve goods from defined storage locations, using equipment like carousels, vertical lift modules, and mini-loaders.
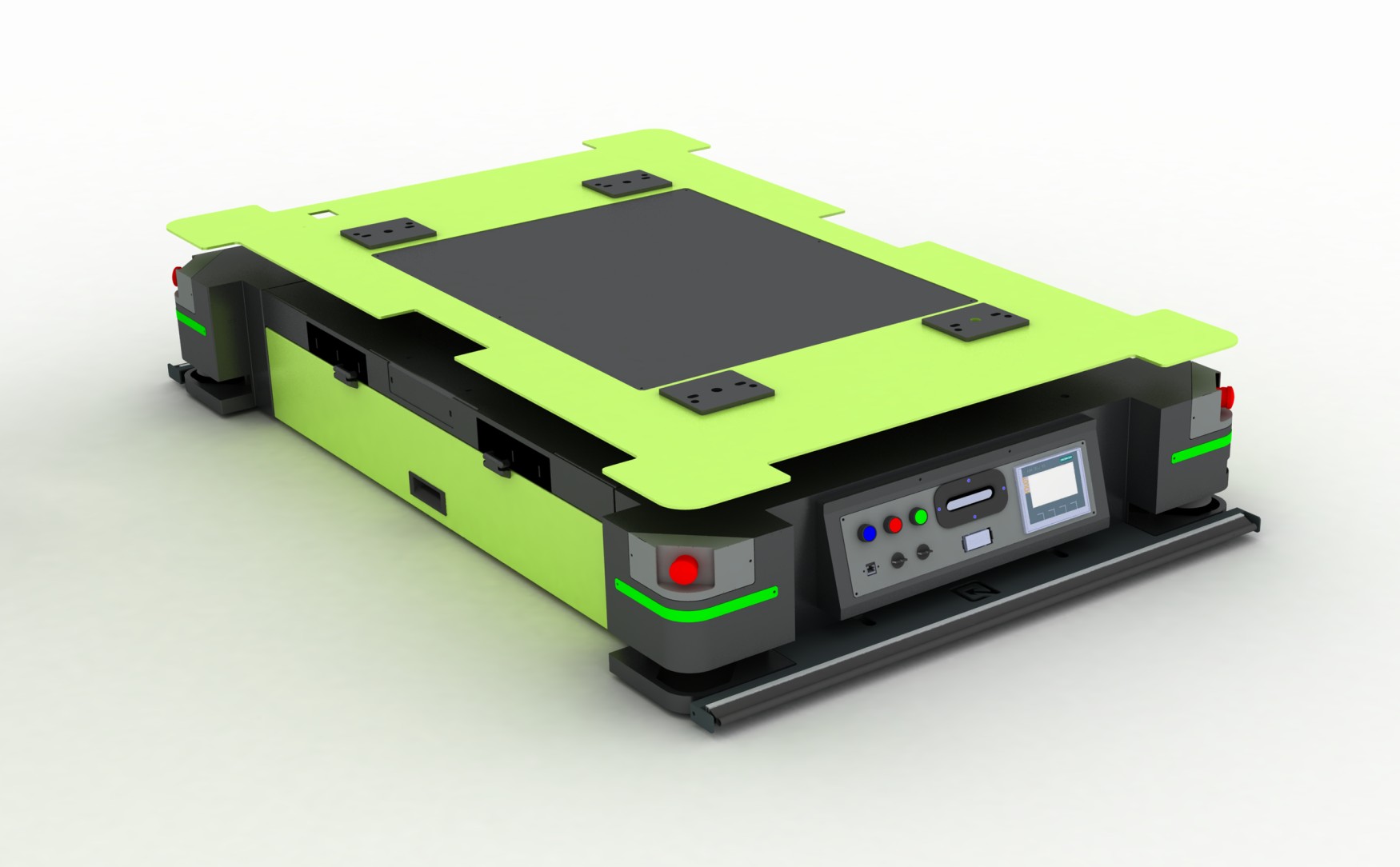
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are mobile robots that transport goods within the warehouse without human intervention, following predetermined paths and equipped with sensors to avoid obstacles.
- Robotic Picking Systems: These systems use robots to pick items from shelves and place them into containers for shipping, significantly speeding up the picking process and reducing errors.
Benefits of Warehouse Automation
The benefits of warehouse automation are substantial and can significantly enhance the efficiency and profitability of warehouse operations.
Increased Efficiency: Automated systems can perform tasks faster and more accurately than human workers, leading to significant improvements in productivity and throughput.
Enhanced Accuracy: Automation minimizes the risk of human error in tasks such as picking, packing, and inventory management, resulting in higher order accuracy and reduced incidence of returns and customer complaints.
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in automation can be high, the long-term cost savings are considerable, as automation reduces labor costs, minimizes waste, and improves resource utilization.
Scalability: Automated systems can be scaled up or down to meet changing business needs, allowing companies to respond quickly to market demands and seasonal fluctuations without significant manual intervention.
Improved Safety: Automation reduces the need for manual handling of goods, minimizing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries, leading to a safer working environment.
Better Space Utilization: Automated systems can optimize warehouse space use, with technologies like vertical lift modules and AS/RS systems making use of vertical space to store more goods in the same footprint.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: With automation, warehouses can process orders more quickly and accurately, leading to faster shipping times and fewer errors, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When to Automate Your Warehouse
Determining the right time to automate your warehouse depends on several factors:
- High Labor Costs: If labor costs are significantly high, automating repetitive tasks can lead to substantial savings.
- Increased Demand: During periods of increased demand or rapid business growth, automation can help scale operations efficiently.
- Frequent Errors: High rates of errors in order fulfillment and inventory management can justify the need for automated systems.
- Space Constraints: If you are running out of storage space, automation can optimize the existing space and delay the need for expansion.
Challenges of Warehouse Automation
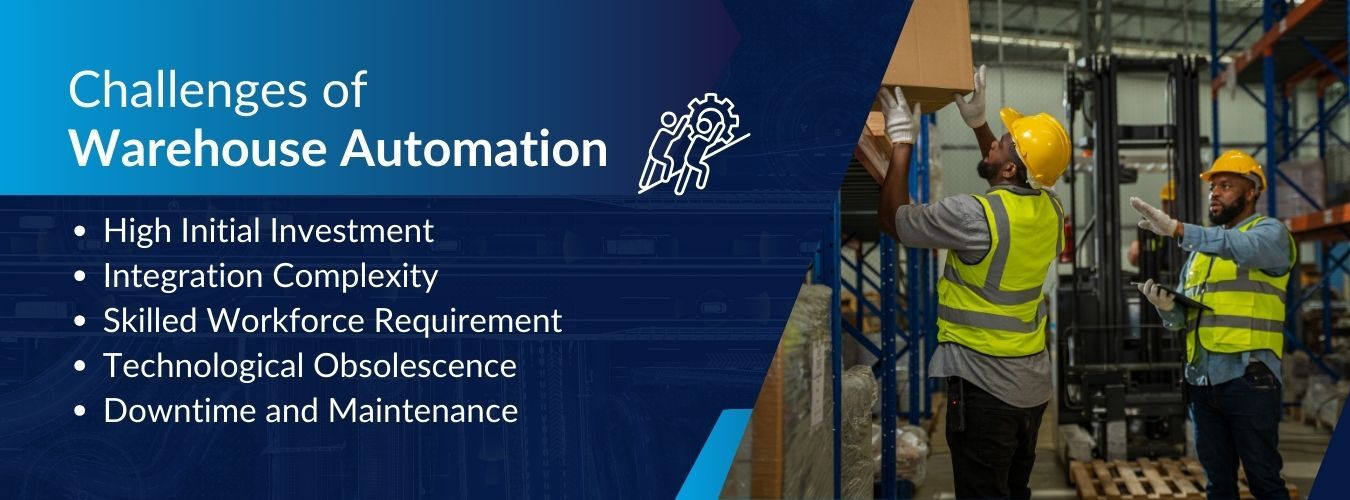
While warehouse automation offers numerous benefits, its implementation comes with several challenges:
High Initial Investment: The cost of procuring and installing automated systems can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Integration Complexity: Integrating automated systems with existing warehouse operations and legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring seamless communication between different technologies.
Skilled Workforce Requirement: Operating and maintaining automated systems require specialized skills, necessitating investment in training or hiring skilled technicians.
Technological Obsolescence: Rapid advancements in technology mean that automated systems can become outdated quickly, requiring frequent upgrades.
Downtime and Maintenance: Automated systems require regular maintenance and are prone to occasional breakdowns, which can disrupt warehouse operations and lead to delays.
Warehouse Automation Market in India
The warehouse automation market in India is witnessing rapid growth, driven by the expanding e-commerce sector, rising consumer expectations, and the government’s push towards modernizing the logistics infrastructure. Key growth factors include:
E-commerce Boom: The exponential growth of India’s e-commerce sector has created a demand for efficient and scalable warehouse solutions to manage the surge in orders.
Government Initiatives: Initiatives such as the Make in India campaign and the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) have streamlined supply chain operations and encouraged investment in automation technologies.
Rise of 3PL Services: The growth of third-party logistics (3PL) providers in India has also contributed to the adoption of warehouse automation, as they use automation to enhance their service offerings.
Urbanization and Smart Cities: The rapid urbanization and development of smart cities in India are fueling the demand for advanced warehouse solutions, with automation playing a crucial role in meeting these needs.
Conclusion
Warehouse automation is transforming the logistics and supply chain landscape by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. While the initial investment and implementation challenges can be significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh these obstacles. In India, the warehouse automation market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the e-commerce boom, government initiatives, technological advancements, and increasing competition.
Novus Hi-tech stands out in this dynamic market, offering state-of-the-art warehouse automation solutions that cater to the specific needs of businesses. Choose Novus Hi-tech for the best in warehouse automation, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
FAQs
What Is Physical Automation in the Warehouse? Physical automation involves using machinery and robotics to perform manual tasks such as picking, packing, and transporting goods within the warehouse.
What Is Digital Automation? Digital automation refers to using software systems like WMS, ERP, and ADC to streamline and optimize warehouse operations, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
What Is Warehouse Automation? Warehouse automation encompasses both physical and digital systems designed to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and productivity of warehouse operations.
How Does Warehouse Automation Work? Warehouse automation works by integrating various technologies, including software systems and robotic machinery, to automate tasks traditionally performed by human workers.
Why Should You Automate Your Warehouse? Automating your warehouse can lead to increased efficiency, enhanced accuracy, cost savings, improved safety, and better space utilization.
What Warehouse Processes Can Be Automated? Processes such as inventory management, order picking, packing, transportation of goods, and data collection can be automated to improve efficiency and accuracy.
How Much Does It Cost to Automate Your Warehouse? The cost of automating a warehouse varies depending on the scale and complexity of the systems implemented, ranging from a few thousand to several million dollars.
What Are the Different Types of Warehouse Automation Technologies? Key technologies include Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Automated Data Collection (ADC), Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS), Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and Robotic Picking Systems.
What Are the Steps to Implement Warehouse Automation? Steps include assessing current operations, identifying areas for automation, selecting appropriate technologies, integrating systems, training staff, and continuously monitoring and optimizing performance.
How Does Warehouse Automation Impact Workforce Requirements? Automation can reduce the need for manual labor, but it also requires a skilled workforce to operate and maintain automated systems, necessitating investment in training or hiring skilled technicians.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing Warehouse Automation? Challenges include high initial investment costs, integration complexity, the need for a skilled workforce, technological obsolescence, and maintenance requirements.
How Do You Measure the Success of Warehouse Automation? Success can be measured by improvements in efficiency, accuracy, cost savings, throughput, and customer satisfaction, as well as reduced error rates and downtime.
Can Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs) Benefit from Warehouse Automation? Yes, SMBs can benefit from warehouse automation through increased efficiency, cost savings, and scalability, although the initial investment may be a consideration.
What Are the Future Trends in Warehouse Automation? Future trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, enhanced robotic capabilities, and greater use of data analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization.
What Are the Regulatory and Compliance Considerations for Warehouse Automation? Compliance with safety regulations, data privacy laws, and industry standards is crucial when implementing warehouse automation, requiring regular audits and adherence to best practices.
For the best in warehouse automation solutions, trust Novus Hi-tech to deliver state-of-the-art technology tailored to your business needs, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.