Material handling is a crucial aspect of any warehouse operation, significantly impacting efficiency, safety, and overall productivity. With advancements in technology, automation in material handling has become increasingly important, offering numerous benefits over traditional methods. This blog explores what material handling is, its types, principles, and the importance of automation in optimizing warehouse operations. For additional insights into the latest advancements and best practices, delve deeper into our resources and expertise.
What Is Material Handling?
Material handling involves the movement, protection, storage, and management of materials and products throughout their lifecycle, including manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal stages. It encompasses a range of manual, semi-automated, and automated equipment and systems that facilitate these processes.
Role in Movement, Protection, Storage, and Control: Effective material handling ensures that materials and products are moved safely and efficiently, stored properly to maximize space utilization, protected from damage, and controlled to maintain an accurate inventory and streamline workflow. Material handling encompasses activities such as loading, unloading, lifting, and transporting goods, as well as packaging and sorting materials. Proper material handling methods ensure that products are delivered in the right quantities and conditions, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain operations.
Types of Material Handling Systems
Material handling systems can be broadly categorized into three types: manual, semi-automated, and automated systems.
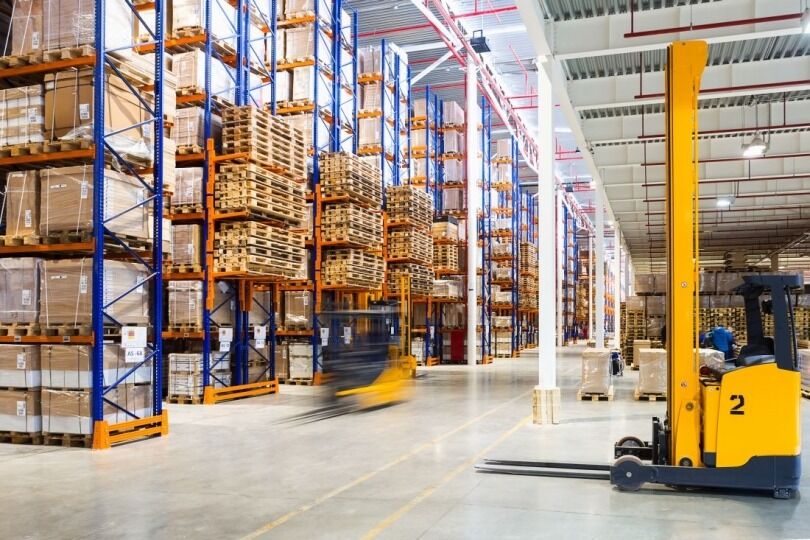
Manual Systems: These systems rely on human labor to move and manage materials. Common examples include hand trucks, pallet jacks, and manual hoists. While manual systems are cost-effective and flexible, they are labor-intensive and may pose higher risks of injury. Manual systems are suitable for smaller operations or for handling lightweight and non-hazardous materials.
Semi-Automated Systems: Semi-automated systems combine human labor with mechanical assistance. Examples include forklifts, conveyors, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) that require some level of human intervention. These systems increase efficiency and reduce physical strain on workers. Semi-automated systems are ideal for medium-sized warehouses and operations that require a balance between automation and human oversight.
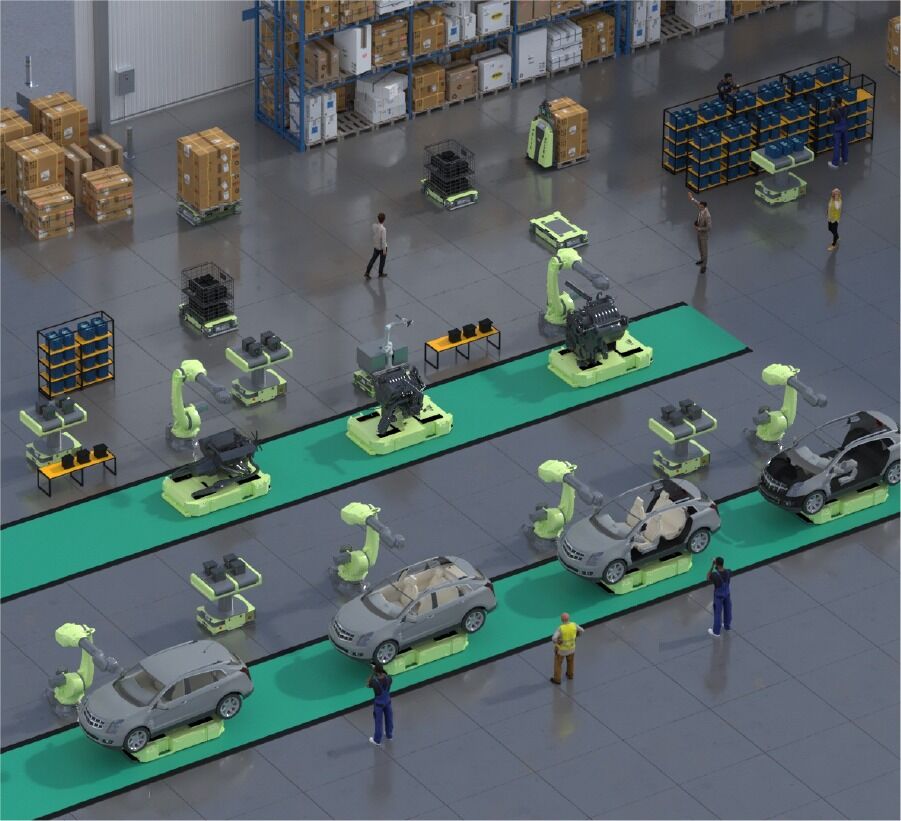
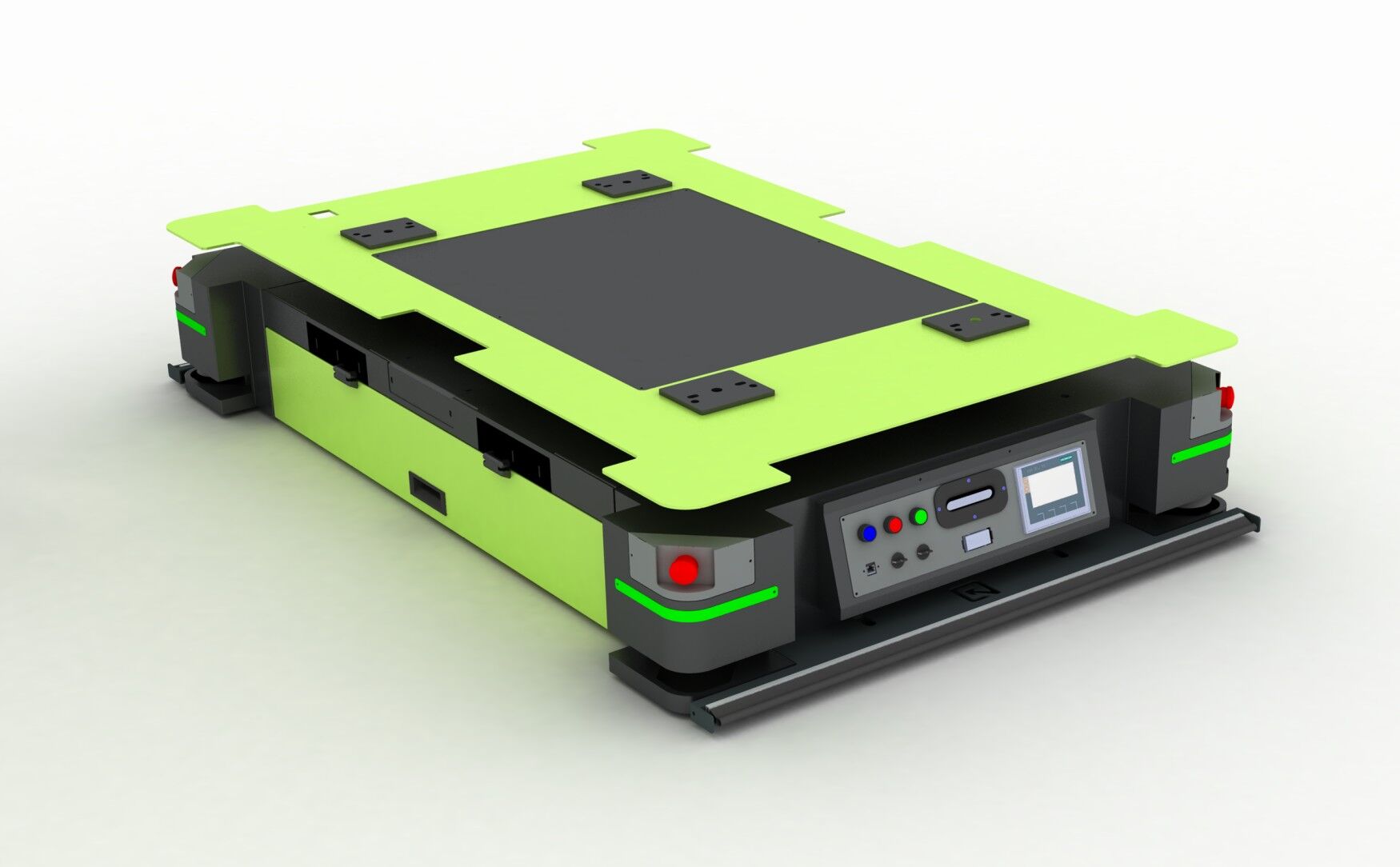
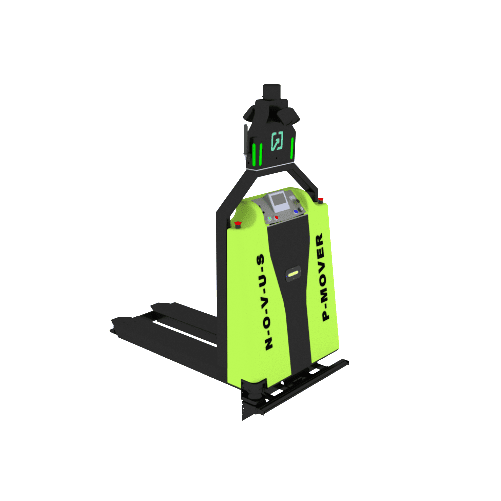
Automated Systems: Automated systems use advanced technologies to perform material handling tasks with minimal human intervention. Examples include robotic arms and fully automated AS/RS. These systems offer the highest levels of efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Automated systems are best suited for large-scale operations that handle high volumes of materials and require consistent and precise handling. A prime example is the Autonomous Battery Operated Pallet Truck from Novus Hi-tech, which streamlines the process of moving heavy loads, reduces manual labor and enhances productivity through advanced navigation and safety features. These specialists in ground-to-ground and ground-to-height material handling usher in a new era of innovative solutions. Experience the future of efficient intra-logistics operations in an autonomous environment and transform your space into a more productive and safer haven.
Importance of Material Handling Automation
The importance of material handling automation cannot be overstated, as it offers significant advantages that transform warehouse operations:
Efficiency and Productivity: Automation increases the speed of material handling processes, allowing for higher throughput and more efficient operations. Automated systems can work continuously without the need for breaks, significantly boosting productivity. This leads to faster processing times and the ability to handle larger volumes of goods, ultimately improving overall warehouse efficiency.
Accuracy and Precision: Automated systems reduce the risk of human error, ensuring that materials are handled and tracked with high precision. This improves inventory management and minimizes discrepancies, leading to more accurate order fulfillment. Advanced technologies such as barcode scanners and RFID tags further enhance tracking accuracy, ensuring that inventory levels are always up-to-date and accurate.
Safety and Risk Reduction: Automation reduces the need for manual handling of heavy or hazardous materials, thereby minimizing the risk of workplace injuries. Automated systems are designed with safety features that further enhance the protection of workers. These features may include sensors, automatic shut offs, and collision avoidance systems, all of which contribute to a safer working environment.
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in automation technology can be substantial, the long-term benefits include reduced labor costs, decreased material damage, and lower operational expenses. Over time, these savings offset the initial costs and contribute to higher profitability. Automation also leads to better resource utilization and reduced waste, further enhancing cost efficiency.
Consistency and Reliability: Automated systems provide consistent performance, ensuring that materials are handled in the same way every time. This consistency enhances the reliability of warehouse operations and ensures predictable outcomes. Consistent processes reduce variability, improve quality control, and ensure that customer expectations are consistently met.
Scalability and Flexibility: Automation systems can be easily scaled to meet changing demands and production volumes. This flexibility allows warehouses to adapt to peak periods and expand operations without significant disruptions. Modular automation solutions can be customized to fit specific operational needs, making it easier to scale up or down as required.
Enhanced Space Utilization: Automated storage and retrieval systems optimize the use of available space, allowing for more efficient storage solutions and better space utilization in the warehouse. Vertical storage options and compact automated systems can significantly increase storage capacity without requiring additional floor space, maximizing the efficiency of existing facilities.
Improved Workflow Integration: Automation can seamlessly integrate with other warehouse management systems, enhancing overall workflow efficiency. This integration allows for real-time data sharing and coordination between different systems, improving decision-making and operational transparency. It ensures that all parts of the warehouse operation are synchronized, reducing delays and bottlenecks.
Environmental Sustainability: Automation contributes to environmental sustainability by optimizing resource use and reducing waste. Energy-efficient automated systems consume less power, and precise handling reduces material waste. These improvements not only lower operational costs but also align with sustainable business practices, reducing the overall environmental footprint of warehouse operations.
Conclusion
Understanding material handling and its importance is crucial for optimizing warehouse operations. The shift towards automation in material handling systems offers significant benefits, including increased productivity, enhanced accuracy, improved safety, and cost savings. Novus Hi-tech provides advanced material handling solutions that integrate automation, ensuring your warehouse operates at peak efficiency. For more details and to explore how we can assist with your specific needs, feel free to reach out to us.
FAQs
1. Benefits of Automated Material Handling Systems:
- Efficiency: Faster sorting, storing, and retrieval.
- Cost Savings: Reduces labor and errors.
- Safety: Minimizes injury risks.
- Space Optimization: Uses vertical storage effectively.
- Scalable: Grows with demand.
2. Improving Efficiency in Material Handling:
- Automation: Use AGVs, conveyors, and robotics.
- Optimized Layout: Store fast-moving items near dispatch.
- Standardization: Streamline processes.
- Training: Enhance workforce skills.
- Data Utilization: Analyze performance to reduce bottlenecks.
3. Key Principles of Material Handling:
- Planning: Align systems with goals.
- Unit Loads: Batch materials for efficiency.
- Ergonomics: Prioritize safety and comfort.
- Automation: Integrate smart tech.
- Sustainability: Reduce waste and energy use.
4. Impact on Warehouse Operations:
- Productivity: Speeds up workflows.
- Inventory Accuracy: Improves tracking.
- Customer Satisfaction: Faster deliveries.
- Cost Efficiency: Lowers operating costs.
- Operational Flow: Streamlines movement and processes.
5. Latest Trends in Automation:
- AI & Robotics: Automates picking and packing.
- AGVs: Autonomous material transport.
- IoT: Real-time tracking and monitoring.
- WMS: Enhances visibility and control.
- Drones: Inventory checks from above.
- Sustainability: Energy-efficient systems.