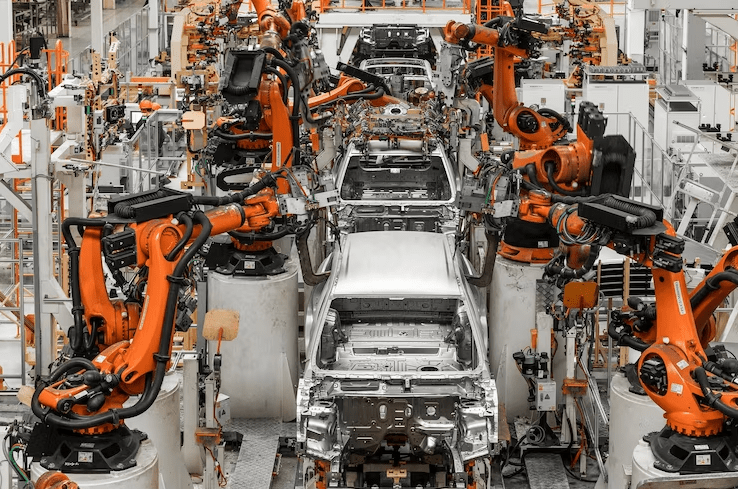
The world of automobile manufacturing, where there are cars assembled with the least human intervention and the precision, speed, and efficiency of vehicle production has drastically changed. This is no longer a futuristic fertility belief—automation in automobile industry. Ranging from AI-powered robotics to advanced machine vision systems, automation means increased concentration of materials, lowered costs, and improved safety. The question is, how is automation changing the auto industry? Let us plunge into the world of smart assemblies and how they are remolding automotive manufacturing.
Key Drivers of Automation in the Automotive Industry
Several important factors chart the course for auto industry automation:
- Efficiency & Productivity: Automation systems work around the clock without tiring, hence yielding greatly bolstered production ranges.
- Cost-wise Advantage: Labour cost and reduced error cut down on cost in vehicle production.
- Security: Robots do jobs that are dangerous, providing a more secure working environment.
- Precision & Quality: Automation makes for an accurate assembly line and fewer defects.
- Scalability: Automation allows manufacturers to rapidly scale production according to demand.
Latest Trends and Innovations in Automotive Automation
The automotive industry is accepting some groundbreaking technical innovations that change the manufacturing and functioning of vehicles. Here are some of the big automation trends that are going on right now:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Automotive Automation: AI plays an essential part in improving various aspects of production and vehicle performance.
- Predictive Facility Maintenance: AI-based systems predict machine failures before events can happen, this in turn reduces downtime.
- Quality Control: The AI-based inspection systems measure parameters that human eyes can’t observe, thus ensuring quality control.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI supports managing logistics, reducing waste, and improving inventory management.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving technology is perhaps one of the biggest developments in automation. Essentially, automation supports self-driving technology by:
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) ensure that a driving experience is safer.
- LiDAR and Computer Vision detect obstacles and provide real-time decisions to continue the drive.
- Machine Learning Algorithms that improve navigation and driving accuracy.
Automation of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
The automation of electric and hybrid vehicles is an emerging aspect to be focused upon in the manufacture of those vehicles, being conducive to environmental preservation:
- Battery Production: Automated systems ensure greater precision in the manufacture of batteries.
- Assembly Line Optimization: Robotics improves efficiency with EV production.
- Smart Charging Infrastructure: AI-driven charging stations upgrade electricity distribution.
Automation System
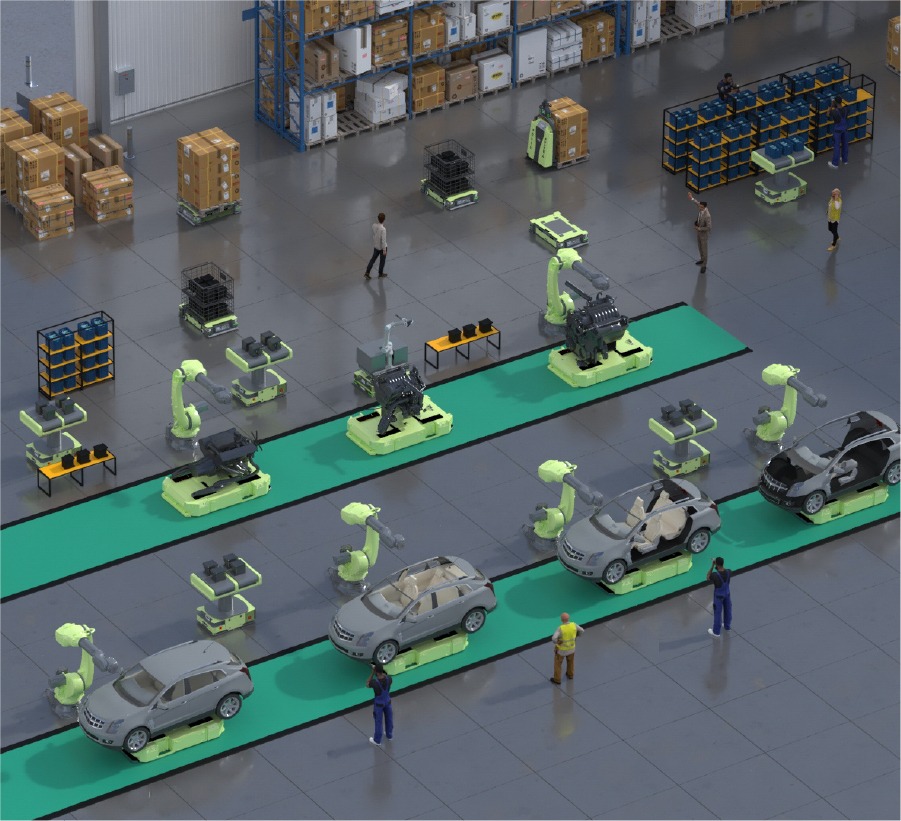
A visible transformation of auto manufacturing processes is occurring through:
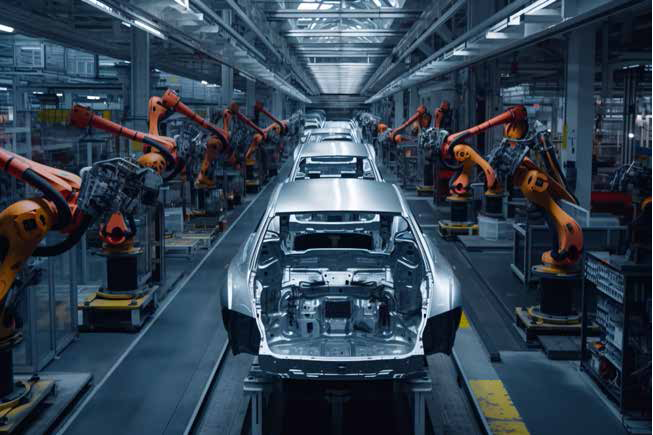
- Robotic Arms assigned for welding, assembly, and painting of high-precision vehicles.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for efficient material transport.
- Flexible production lines are easily changeable for various vehicle models.
Industry 4.0 and Intelligent Manufacturing
With the lines blurring between IoT, big data, and automation, automobile manufacturing is redefined by:
- Connected factories that optimize production using real-time data.
- Digital twins that simulate actual production environments to finally achieve efficiency.
- Cyber-Physical Systems that observe and control manufacturing processes.
Machine Vision for Quality Control
Machine vision technology is simply the revolutionizing formula through complete quality control that constitutes
- AI-driven camera automated defect detection.
- 3D scanning for proper alignment of parts.
- Color and surface inspection in achieving a uniform paint job.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA helps streamline several processes in the automotive industry, including:
- Automating administrative functions related to inventory management and order processing.
- Enhancing product testing through simulation and analysis of test results.
- Optimizing logistics operations from warehouse automation.
Robots and Cobots in Automotive Manufacturing
- Industrial robots perform repetitive tasks like welding and painting.
- Cobots are collaborative robots that work together with people to facilitate increased efficiency and safety.
- Integration into Assembly Lines: Cobots assist with complex tasks that require precision.
Implementation of Automation in Automakers
Many automotive manufacturers, both worldwide and locally, rely on automation for streamlining their manufacturing:
- Tesla: An extensive use of robotic arms within Gigafactories for EV production.
- BMW: AI-based quality control systems to catch defects in manufacturing.
- Toyota: Automated welding and assembly lines for increased efficiency.
Novus Hi-Tech in Automotive Automation
At the forefront of automotive automation, Novus Hi-Tech develops state-of-the-art solutions in:
- ADAS Solutions: Making vehicles safe through driver assistance systems.
- Smart Sensors: Improving vehicle diagnostics and predictive maintenance.
- Automated Inspection Systems: Ensuring high precision in manufacturing.
Future Automation in Automobile Industry
The future of automation seems more promising with such prospectus as:
- Complete Autonomous Manufacturing: Factories with zero human intervention.
- AI-Induced Customization: Car attributes based on preferences from various customers.
- Blockchain Integration: Secure and transparent management of the supply chain.
FAQs
What is the most common robot used in the automotive industry?
Industrial robotic arms, particularly those used for welding and painting, are the most common in the automotive industry.
What are the four most common types of robots?
The four most common types are:
- Articulated Robots (robotic arms with multiple joints)
- SCARA Robots (used for assembly tasks)
- Cartesian Robots (for high-precision operations)
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots) (designed to work alongside humans)
What are the two main advantages that automation brings?
- Increased Efficiency: Automation speeds up production while reducing costs.
- Improved Quality: Automated systems ensure precision and minimize errors.
What are 6-axis robots?
6-axis robots have six degrees of movement, allowing them to perform highly complex tasks like welding, painting, and assembly with great flexibility.