Zone picking is a popular method used in warehouses to increase efficiency and accuracy in order fulfillment processes. This method involves dividing the warehouse into zones, with each zone assigned to specific pickers responsible for picking items only within their designated area. This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide to zone picking, including its definition, key benefits, implementation considerations, and advanced techniques.
What is Zone Picking?
Zone picking is a warehouse management strategy where the picking process is divided into zones, and each picker is assigned to a specific zone. This method is particularly effective in warehouses with high-volume orders and a wide range of products. By dividing the picking process into smaller, more manageable tasks, zone picking can significantly reduce picking time and improve accuracy.
Key Benefits of Zone Picking
- Improved Efficiency: Zone picking improves efficiency by dividing the picking process into smaller, more manageable tasks. By assigning pickers to specific zones and organizing the warehouse layout to minimize picker travel time, zone picking reduces the time and effort required to pick orders, leading to faster order fulfillment.
- Increased Accuracy: Zone picking helps improve picking accuracy by reducing the likelihood of errors. By assigning pickers to specific zones and making them responsible for picking items only within their designated area, zone picking reduces the chances of picking the wrong items or quantities, leading to fewer errors and improved order accuracy.
- Reduced Picking Time: Zone picking reduces picking time by optimizing picker routes and minimizing picker travel time. By assigning pickers to specific zones and organizing the warehouse layout to minimize the distance they need to travel, zone picking reduces the time it takes to pick orders, leading to faster order fulfillment.
- Lower Labor Costs: Zone picking can help reduce labor costs by optimizing picker routes and reducing picker travel time. By assigning pickers to specific zones and organizing the warehouse layout to minimize the distance they need to travel, zone picking reduces the amount of time pickers spend picking orders, leading to lower labor costs.
- Increased Order Throughput: Zone picking increases order throughput by optimizing the picking process. By dividing the picking process into smaller, more manageable tasks and assigning pickers to specific zones, zone picking allows warehouses to process more orders in less time, leading to increased order throughput and improved customer satisfaction.
Discover how Zone Picking optimizes warehouse operations and productivity.
Download our free brochure for expert insights and trends!
When to Consider Zone Picking
Zone picking is most suitable for warehouses with high-volume orders, a wide range of products, and a need for improved picking efficiency and accuracy. It is also beneficial for warehouses with limited space, as it optimizes the use of available space and reduces congestion in high-traffic areas.
- High Volume Orders: Zone picking is particularly beneficial for warehouses that handle high volumes of orders. By dividing the picking process into zones and assigning pickers to specific areas, warehouses can process orders more quickly and efficiently, leading to faster order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction.
- Wide Range of Products: Warehouses that stock a wide range of products can also benefit from zone picking. By assigning pickers to specific zones based on product characteristics such as size, weight, and demand, warehouses can optimize the picking process and reduce picker travel time, leading to increased efficiency and accuracy.
- Need for Improved Efficiency and Accuracy: Zone picking is ideal for warehouses that need to improve the efficiency and accuracy of their picking operations. By dividing the picking process into smaller, more manageable tasks, zone picking can help warehouses reduce picking errors and improve overall picking performance.
- Limited Space: Warehouses with limited space can also benefit from zone picking. By organizing the warehouse into zones and optimizing the layout to minimize picker travel time, warehouses can make better use of available space and reduce congestion in high-traffic areas.
- Variable Order Profiles: Warehouses with variable order profiles, such as those that experience seasonal fluctuations in demand or have a mix of large and small orders, can benefit from zone picking. By adjusting the number and size of zones based on order profiles, warehouses can optimize the picking process and improve overall efficiency.
- Desire to Reduce Labor Costs: Zone picking can help warehouses reduce labor costs by optimizing picker routes and reducing picker travel time. By assigning pickers to specific zones and optimizing the layout of the warehouse, warehouses can minimize the amount of time pickers spend moving between locations, leading to reduced labor costs.
Overall, warehouses should consider zone picking when they need to improve the efficiency and accuracy of their picking operations, handle high volumes of orders, stock a wide range of products, have limited space, experience variable order profiles, or desire to reduce labor costs. By carefully evaluating these factors, warehouses can determine if zone picking is the right solution for their operation.
Factors to Consider for Implementation
- Warehouse Size and Layout: The size and layout of the warehouse play a crucial role in determining the number and size of zones needed for zone picking. A larger warehouse may require more zones to efficiently handle the picking process, while a smaller warehouse may have fewer zones but require careful layout planning to ensure optimal flow and minimal picker travel time.
- Product Variety and Volume: The variety and volume of products in the warehouse will influence how zones are assigned and organized. Products with high demand or that are frequently ordered together may be grouped in the same zone to reduce picker travel time and increase efficiency. Similarly, products that are bulky or require special handling may be assigned to specific zones with trained personnel.
- Order Profile and Fulfillment Requirements: Understanding the profile of orders, such as their size, frequency, and urgency, is crucial for designing an effective zone picking system. For example, if the majority of orders are small but frequent, batch picking may be more efficient than single-order picking. Additionally, if orders require expedited fulfillment, zones may be organized to prioritize these orders.
- Warehouse Technology and Infrastructure: The implementation of zone picking may require upgrades or additions to the warehouse’s technology and infrastructure. This could include implementing a warehouse management system (WMS) to track inventory and orders, as well as integrating automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) or pick-to-light and voice-directed picking systems to improve efficiency and accuracy.
- Staffing and Training: Implementing zone picking will require selecting and training pickers to work within their assigned zones. Pickers will need to be familiar with the products in their zone, as well as the picking strategies and workflows specific to their area. Additionally, supervisors and managers will need to be trained to oversee and optimize zone picking operations.
- Performance Measurement and Evaluation: To ensure the success of zone picking, warehouses should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the efficiency and accuracy of the picking process. KPIs may include picking accuracy rates, picking speed, labor costs, and order fulfillment lead times. By monitoring these metrics, warehouses can identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to optimize zone picking operations.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Finally, when implementing zone picking, warehouses should consider the scalability and flexibility of the system. As the business grows and order volumes increase, the zone picking system should be able to accommodate these changes. Additionally, the system should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in product mix, order profiles, and fulfillment requirements.
By carefully considering these factors, warehouses can effectively plan and implement a zone picking system that meets their specific needs and improves efficiency and accuracy in order fulfillment processes.
Case Studies: Examples of Successful Zone Picking Implementations
Planning and Implementing Zone Picking
- Warehouse Layout and Zone Design: Designing the layout of the warehouse and dividing it into zones based on product characteristics, such as size, weight, and demand.
- Optimizing Zone Layout: Arranging zones to minimize picker travel time and optimize the flow of goods through the warehouse.
- Picking Strategies and Workflows: Implementing batch picking or single-order picking strategies based on order profiles and fulfillment requirements.
- Integration with WMS: Integrating zone picking with warehouse management systems (WMS) to track inventory, orders, and picker performance.
- Staffing and Training: Selecting and training pickers to ensure they are efficient and accurate in their assigned zones.
- Performance Measurement and Evaluation: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of zone picking and identify areas for improvement.
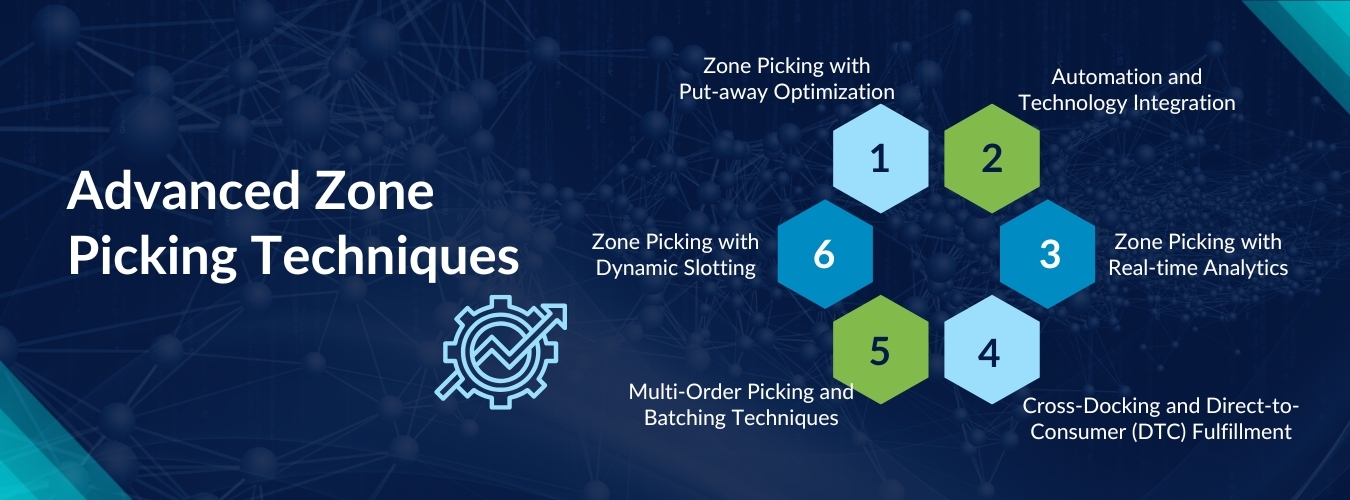
Advanced Zone Picking Techniques
- Zone Picking with Put-away Optimization: This technique involves integrating the picking and put-away processes to improve overall warehouse efficiency. By coordinating the timing of put-away tasks with picking activities, warehouses can reduce the distance traveled by pickers and optimize the flow of goods through the warehouse. This can lead to faster order fulfillment and reduced labor costs.
- Multi-Order Picking and Batching Techniques: Multi-order picking involves picking items for multiple orders simultaneously, while batching involves grouping orders together to be picked as a batch. These techniques can significantly improve picking efficiency and reduce picker travel time. By carefully grouping orders based on their location in the warehouse and the items required, warehouses can minimize the number of trips pickers need to make and increase order throughput.
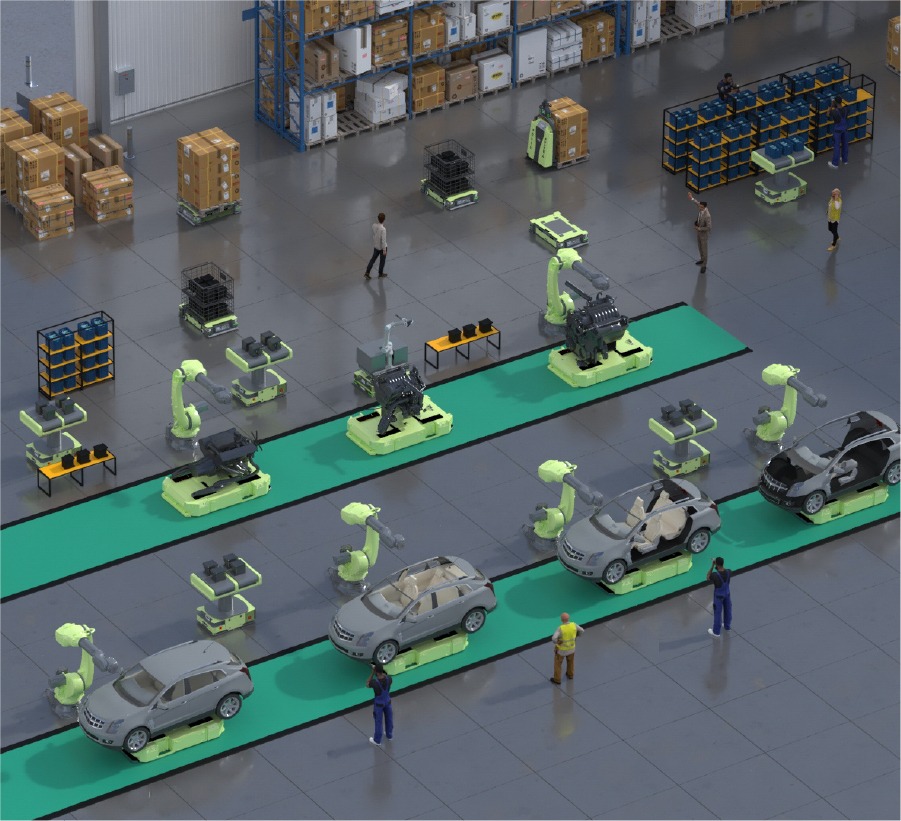
- Automation and Technology Integration: Automation technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), pick-to-light systems, and voice-directed picking systems can further optimize zone picking operations. AS/RS can automatically retrieve items from storage locations, reducing the need for manual picking. Pick-to-light and voice-directed picking systems can provide pickers with real-time picking instructions, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Zone Picking with Dynamic Slotting: Dynamic slotting involves continuously adjusting the location of items in the warehouse based on demand patterns and other factors. By dynamically slotting items based on their popularity and picking frequency, warehouses can reduce picker travel time and improve overall picking efficiency. This technique requires sophisticated inventory management and slotting algorithms to optimize slotting decisions.
- Cross-Docking and Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Fulfillment: Cross-docking involves transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound docks without storing them in the warehouse. This technique can significantly reduce order fulfillment lead times and improve overall efficiency. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) fulfillment involves shipping orders directly from the manufacturer or supplier to the end customer, bypassing the warehouse altogether. Both techniques can be integrated with zone picking to further streamline the order fulfillment process.
- Zone Picking with Real-time Analytics: Real-time analytics can provide warehouses with valuable insights into their picking operations, allowing them to identify bottlenecks, optimize picking routes, and improve overall efficiency. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as picking accuracy, speed, and labor costs in real-time, warehouses can make data-driven decisions to continuously improve their zone picking operations.
Conclusion
Zone picking is a highly effective warehouse management strategy that can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy in order fulfillment processes. By dividing the picking process into zones and assigning pickers to specific areas, warehouses can reduce picking time, lower labor costs, and increase order throughput. Implementing zone picking requires careful planning and consideration of factors such as warehouse size, product variety, and order profile. By following the guidelines outlined in this blog post, warehouses can successfully implement zone picking and achieve their efficiency goals.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between zone picking and batch picking?
Zone Picking is a method where the warehouse is divided into zones, and each picker is assigned to a specific zone. They only pick items within their zone, and the order moves from one zone to another until it’s complete.
Batch Picking involves a picker collecting items for multiple orders in one trip. It’s efficient for high-volume, small-item orders as it reduces travel time.
Key Difference:
- Zone Picking is optimized by area (pickers stay in one place).
- Batch Picking is optimized by quantity (pickers handle multiple orders at once).
2. What is the biggest challenge with zone picking?
The biggest challenge with zone picking is coordinating and consolidating orders across multiple zones. Since each zone picks only part of an order, the process requires an efficient system to bring all items together accurately and on time, which can complicate fulfillment and increase chances of delay or error.
3. What is the golden zone for picking?
The Golden Zone refers to the area between a picker’s shoulder and waist height. Items stored in this zone are the easiest and fastest to access, minimizing bending or reaching. Warehouses often store fast-moving or high-demand items in the golden zone to increase picking speed and reduce fatigue.
4. What are the three strategies of picking in warehousing?
The three main picking strategies are:
- Piece Picking (Discrete Picking) – Picking one order at a time, item by item. Ideal for small operations.
- Batch Picking – Picking multiple orders simultaneously to minimize travel time.
- Zone Picking – Assigning pickers to specific zones where they pick items for any order passing through their area.
Some warehouses also use Wave Picking, which combines elements of all three, releasing orders in waves based on shipping schedules.